Bacterial folliculitis is a common scalp infection. It’s usually caused by bacteria that live on our skin. Though it’s widespread, many people don’t know about the different types and how to treat them. This can lead to red, itchy bumps. If not treated, these can cause permanent hair loss or scars.
In this article, we dive into 8 types of scalp folliculitis and ways to treat them. We’ll look at symptoms, causes, and treatments. Our goal is to help you have healthier hair and scalp.
Key Takeaways
- Bacterial folliculitis is the most common form and usually resolves without treatment.
- There are 8 different types of scalp folliculitis, each requiring specific management techniques.
- Hot tub folliculitis typically clears up within two weeks without antibiotics.
- Individuals with weakened immune systems are at higher risk for these scalp infections.
- Regularly using antifungal shampoos can help prevent seborrheic dermatitis.
- Localized folliculitis may respond well to antibiotic cream, while severe cases might necessitate oral medication.
What Is Scalp Folliculitis?
Scalp folliculitis is the swelling of hair roots on the scalp. This scalp skin condition is often due to bacteria or fungi. It causes symptoms like small, red bumps that look similar to acne. The most common cause is the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus.
The swelling may come from many factors, including skin infections and ingrown hairs. Sometimes, even certain medicines can lead to it. People who have taken antibiotics might get gram-negative folliculitis. Also, eosinophilic folliculitis is more usual in men.
Knowing the signs early and getting help is key to handle this issue well. While mild cases may get better with over-the-counter products, like special shampoos, tougher cases might need stronger medicines. Understanding scalp folliculitis and making good choices can help keep your scalp healthy.
Washing your scalp regularly and avoiding tight hats can lower your chances of getting this painful condition. For more scalp care tips, click on this link.
What Does Scalp Folliculitis Look Like?
Scalp folliculitis looks like small red bumps in clusters. These are like acne and filled with pus. Some bumps can get bigger, turn into inflamed lesions, or have crusty sores on them. If it’s a mild case, you might see whiteheads on the bumps, which means there might be an infection.
When the condition gets worse, it can hurt and feel like burning. Blisters might also form and leak fluid if they break. This adds to the discomfort and worry of having such a condition.
It’s important to know that symptoms vary depending on how severe the folliculitis is. The way it looks can change based on your skin type and health conditions. People may see different levels of redness and swelling. Some may need a doctor’s care if the lesions are very severe.
| Type of Lesion | Description | Pus Presence |
|---|---|---|
| Red Bumps | Small clusters, often itchy. | Yes |
| Whiteheads | Fluid-filled bumps found in some cases. | Yes |
| Crusty Sores | Indicate secondary infection or irritation. | Varies |
| Blisters | May occur and are prone to oozing. | Yes |
Symptoms of Scalp Folliculitis
Scalp folliculitis is shown by clusters of pus-filled bumps on the scalp. These bumps may hurt and cause an itchy scalp condition. The skin area can turn red and swell up, looking like small whiteheads.
Soreness and a mild fever can also be symptoms. Identifying these signs early helps in seeking the right treatment fast. A website to find more on this is effective treatment methods available. Many types of folliculitis exist but the pus-filled bumps are a common sign among them.
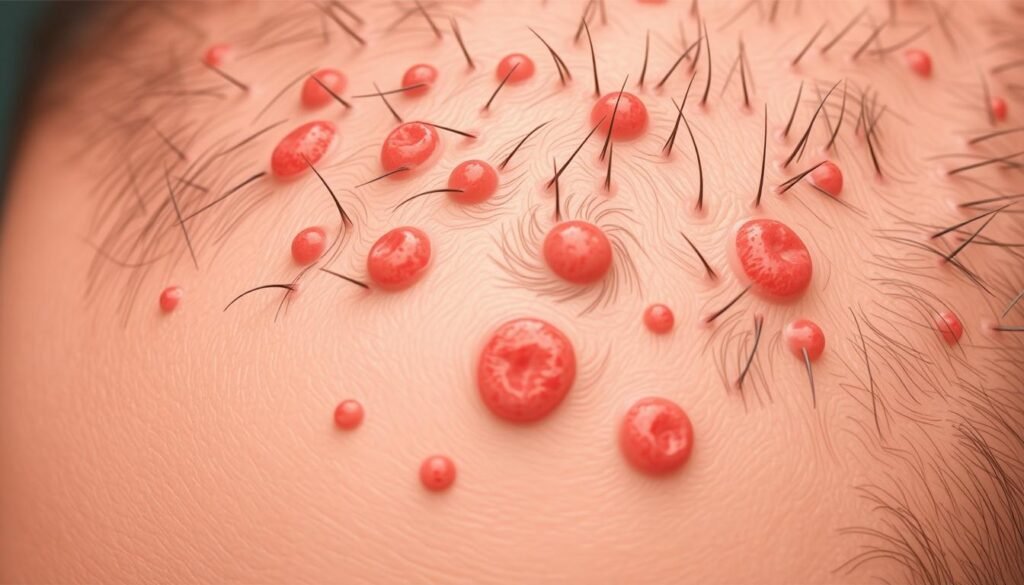
Though many folliculitis cases are mild, spotting symptoms early aids in treatment. Knowing all the symptoms helps people decide the best action for relief.
8 Types of Scalp Folliculitis & Ways to Get Rid of Them
Scalp folliculitis appears in different ways, affecting people uniquely. Knowing the variations helps in choosing the right treatment. It splits into two groups: superficial and deep folliculitis.
Superficial Folliculitis
Superficial folliculitis shows as slight redness or tiny pus bumps. It’s mainly caused by bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus or too much yeast. Things like ingrown hairs or tight clothes can also trigger it.
Usually, it gets better in a few weeks. Topical antibiotics or special shampoos can aid recovery.
Deep Folliculitis
Deep folliculitis, on the other hand, can be more severe. It can turn into painful boils or abscesses. Conditions include eosinophilic folliculitis and acne necrotica, which can scar without treatment.
Treatments may involve oral antibiotics or more advanced methods. The goal is to relieve symptoms and promote hair growth.
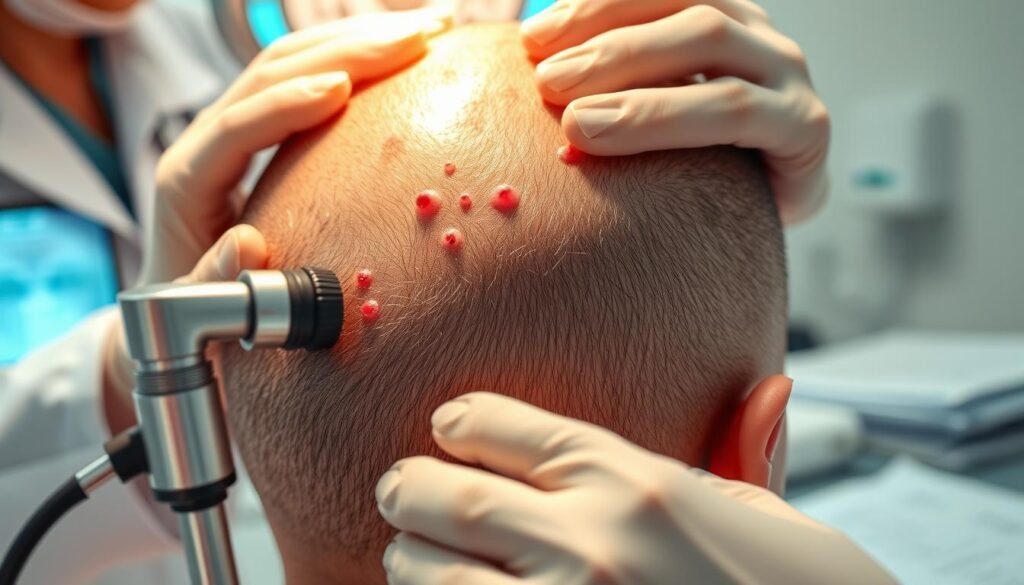
How Is Scalp Folliculitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing scalp folliculitis starts with a full medical check-up. A healthcare expert will do a physical exam. They will also ask about your medical history and symptoms. The doctor will carefully look at the scalp areas that are affected.
Sometimes, more tests are needed. These might include lab tests or swab cultures to find the cause of the folliculitis. For bacterial infections, like those from Staphylococcus aureus, specific tests are done to confirm. Skin biopsies are only done if really needed, to check for other skin problems that look like folliculitis.
Knowing these steps helps in planning the right treatment. If you think you have a scalp issue, it’s key to get checked out. A medical evaluation is the first step.
| Diagnostic Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Visual inspection of the scalp and other affected areas to assess symptoms. |
| Medical History Review | Gathering information about existing health conditions and past skin issues. |
| Swab Cultures | Testing samples from the scalp to identify the specific bacteria or fungi causing the infection. |
| Skin Biopsy | Rarely performed, this procedure helps rule out other skin conditions. |
What Causes Folliculitis on the Scalp?
Scalp folliculitis comes from different factors that target hair follicles. Wearing tight hats or helmets are common causes. Frequent shaving can harm follicles and lead to inflammation. Too much use of some hair products adds to the risk by clogging and irritating the follicles.
Infectious agents play a big part in hair follicle infections. Bacteria, especially Staphylococcus aureus, are often to blame. Yeast infections by Malassezia species can also cause issues. Those who use medicines for epidermal growth might see severe skin reactions, like drug-related breakouts.
People with weak immune systems or conditions like diabetes can get folliculitis easier. Special cases, like gram-negative folliculitis, happen with long-term antibiotic use. For example, Pseudomonas aeruginosa can cause hot tub folliculitis. This shows why clean swimming places are essential.
Knowing what leads to scalp folliculitis helps in preventing and treating it. Good hair care and avoiding irritants make for a healthier scalp. For help with scalp problems, Neofollics’ scalp treatment products are a solid choice.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Irritants | Tight hats, helmets, and frequent shaving damage follicles. |
| Bacterial Infections | Primarily caused by Staphylococcus aureus. |
| Yeast Infections | Malassezia species causing inflammation. |
| Medication Effects | Epidermal growth factor inhibitors leading to drug eruption. |
| Immune System | Individuals with weakened immune systems are at higher risk. |
| Environmental Factors | Exposure to contaminated water causing hot tub folliculitis. |
How Do You Treat Scalp Folliculitis?
To treat scalp folliculitis, use medication and change your lifestyle. Begin with topical treatments to fight inflammation and infection. Topical antibiotics like clindamycin or fusidic acid often reduce symptoms quickly. These target the bacterial infections causing the condition.
Topical Antibiotics
Topical antibiotics are key for initial treatment. They can show results in a week, ideal for mild cases. Often prescribed are:
- Clindamycin
- Fusidic acid
- Gentamicin
These antibiotics lower redness and swelling, helping you recover faster.
Oral Medications
If the situation is severe or keeps coming back, oral antibiotics might be needed. This step helps when topical treatments don’t work or the infection spreads. Common oral antibiotics include:
- Doxycycline
- Minocycline
- Augmentin
A doctor will decide if you need oral medications, which greatly help with scalp folliculitis. Remember, avoiding tight hairdos, using gentle shampoos, and maintaining scalp cleanliness are also vital to prevent future problems.
| Type of Treatment | Examples | Administration Method | Expected Time for Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical Antibiotics | Clindamycin, Fusidic Acid | Applied directly to the affected areas | 7 to 10 days |
| Oral Antibiotics | Doxycycline, Minocycline | Taken orally as prescribed | Varies; often several weeks |
Prevention Tips for Scalp Folliculitis
To stop scalp folliculitis, keeping clean is key. Wash your hair regularly with a gentle, sulfate-free shampoo. This keeps the scalp clean and fights bacteria. It’s also important not to share towels and razors, as they can spread the bacteria that cause folliculitis.
Using fewer hair products can also help. Products clogging hair follicles can lead to infections. Be careful with tight helmets or hats, as they can irritate your scalp. This irritation can make folliculitis worse.
For those with diabetes or weak immune systems, seeing a healthcare provider regularly is wise. They can help you keep your scalp healthy. Catching signs early and taking steps to prevent can be very helpful.
Following these scalp care tips can keep your scalp healthy and free from folliculitis. Focus on key aspects like:
- Maintaining proper hygiene.
- Avoiding shared personal items.
- Minimizing hair product usage.
- Avoiding tight headgear.
- Consulting a healthcare professional for chronic conditions.
By paying attention to these points, you can lower your risk of getting scalp folliculitis. Keeping your hair and scalp healthy is possible.
| Prevention Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| Hygiene | Wash hair regularly with gentle shampoo. |
| Avoid Sharing | Never share personal items like towels or razors. |
| Limit Products | Use fewer hair products that can clog follicles. |
| Avoid Tight Gear | Refrain from wearing tight helmets or hats for long periods. |
| Consult Professionals | Seek medical guidance for preexisting conditions. |
Conclusion
Scalp folliculitis is a condition many people deal with. It causes inflammation in the hair follicles. By learning about its types, symptoms, and causes, people can get the right help when needed. Knowing the signs helps in choosing how to treat it and prevent it, leading to a healthier scalp.
There are effective treatments for scalp infections. These include medical treatments and things you can do at home. Using antifungal shampoos can help a lot, and warm compresses might reduce swelling and pain. It’s important to know that with the right care, about 92% of people see a better scalp in 28 days.
Keeping a healthy scalp means getting help when you need it and knowing how to take care of your hair. Whether you’re preventing problems or getting advice from experts, acting quickly against scalp folliculitis is key. This way, people can have a healthier scalp and feel better overall.