Did you know that over 80% of people will get a skin condition at some point? This condition affects hair follicles. It can range from minor irritations to severe infections. Folliculitis is common and must be well understood by healthcare providers. This is especially true for correct medical coding.
The ICD-10 folliculitis codes are crucial. They help in diagnosing, treating, and reimbursing care for this ailment.
Getting the medical coding right is key for correctly diagnosing and treating folliculitis. Each code, like L66.2 for a specific form or L73.9 for an undetermined acne-like disorder, tracks patient health and affects reimbursement. Healthcare workers need to know these codes. This knowledge allows them to give better care and avoid issues.
Knowing about folliculitis and its signs early is important. It helps with patient care and efficiency in medical settings. To learn more about spotting and treating this common problem, click here.
Key Takeaways
- Folliculitis impacts over 80% of individuals at some point, showing its significance in healthcare.
- Right ICD-10 folliculitis coding matters a lot for diagnosing and treating patients effectively.
- Inflamed bumps around hair follicles are common signs that need quick action.
- There are many treatments, like topical antibiotics and antifungal creams.
- Knowing the different codes makes medical billing smoother.
Understanding Folliculitis
Folliculitis is an issue where hair follicles get inflamed or infected. It leads to various symptoms. The condition has many causes and types, depending on what’s behind it.
Definition and Symptoms
Folliculitis symptoms often include red, swollen bumps near hair follicles. People might feel itchiness, soreness, and see pus-filled blisters. Sometimes, the skin crusts over.
Risk factors for folliculitis include not keeping clean, wearing tight clothes, shaving, and hot tub use. Having skin problems like eczema raises the risk, too.
Types of Folliculitis
Folliculitis has several types, each with its own features:
- Bacterial Folliculitis: Staphylococcus aureus bacteria cause this common type.
- Fungal Folliculitis: Happens because of yeast infections.
- Viral Folliculitis: Viruses cause this, leading to special symptoms and care.
- Keloidal Folliculitis: Mainly seen in black patients, it results in big scars.
- Folliculitis Decalvans: Scarring leads to hair loss over time.
- Acneiform Folliculitis: Certain medicines can trigger this type.
- Toxic Erythema of the Newborn: Shows up in newborns soon after birth.
- Pruritus Folliculitis of Pregnancy: Hits pregnant women, showing it can affect anyone.
Knowing the types of folliculitis helps diagnose and treat it right. Each type needs a different approach to stop it from coming back. Seeing a doctor regularly and learning about the condition are key to control.
What is the ICD-10 Classification?
The ICD-10 system is key for medical coding. It organizes diseases and health issues for better diagnosis. For issues like folliculitis, it’s very important. Each ICD-10 code matches specific conditions. This ensures doctors identify and classify them correctly.
Folliculitis coding is placed under skin conditions. It’s organized well to help with accurate reporting and treatment plans. The ICD-10 helps doctors describe a patient’s condition clearly. This makes tracking treatment results and effectiveness easier.
Here’s a detailed table showing how ICD-10 classifies skin-related conditions:
| ICD-10 Code | Description | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| L73.0 | Folliculitis | Redness, swelling, and pus-filled bumps |
| L72.0 | Follicular cyst | Small bumps under the skin |
| L70.0 | Acne vulgaris | Comedones, papules, pustules, or cysts |
| L70.8 | Other acne | Various lesions on the skin |
| L70.9 | Acne, unspecified | Broad range of acne symptoms |
This method not only improves medical coding but ensures treatments match the right diagnoses. This is great for patient care.
ICD-10 Folliculitis Overview
Understanding folliculitis is key to its proper diagnosis and treatment. In the realm of the ICD-10 Folliculitis Overview, coding accurately is crucial. It ensures healthcare providers can manage this skin issue effectively. Proper coding helps patients get the right treatment. It also avoids misdiagnosis.
Importance of Accurate Coding
Accurate coding is critical in medical billing. It allows for correct payment for services. It also helps in following patient outcomes. Errors in coding can delay treatment or cause billing issues. This puts patient care and healthcare finances at risk. Healthcare workers must know the ICD-10 codes for folliculitis. This knowledge supports effective treatment.
Common Symptoms Associated with Folliculitis
Recognizing folliculitis symptoms helps in early diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms often include:
- Red, swollen bumps on the skin
- Itching, affecting roughly 80% of patients
- Tenderness in the affected spots
- Pain that can get worse with tight clothes
These symptoms are common. Yet, around 5-10% of cases might see complications like cellulitis. This needs stronger treatment. Knowing these signs helps doctors act fast.
| Symptom | Percentage of Patients Affected |
|---|---|
| Itching | 80% |
| Swollen Bumps | Approx. 70% |
| Tenderness | 66% |
| Pain | 55% |
ICD-10 Codes Used for Folliculitis
It’s key to know the right codes for diagnosing folliculitis. This ensures doctors provide the right care and get proper payment. Here’s a look at the codes for different types of folliculitis.
Billable ICD-10 Codes
For billing, several ICD-10 codes cover folliculitis. Here’s a list of important codes used in medical billing:
| ICD-10 Code | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| L66.2 | Folliculitis decalvans | Folliculitis Type |
| L73.9 | Acneiform disorder, unspecified | Folliculitis Type |
| L71.9 | Rosacea, unspecified | Related Condition |
| L72.0 | Epidermal cyst | Related Condition |
| L72.1 | Pilar and trichodermal cyst | Related Condition |
Specific Codes for Different Types of Folliculitis
Knowing the different folliculitis types helps with coding and treatment. Each code matches a specific folliculitis type. This helps doctors care for patients better and follow billing rules.
Recognizing Folliculitis Diagnosis Code
It’s very important to identify folliculitis correctly for the right treatment and claims. Medical experts use certain standards to record folliculitis accurately with the right diagnosis code. The folliculitis diagnosis code is key, as it gives a standard way to note the condition in medical records and billing.
Criteria for Diagnosis
Diagnosing folliculitis requires key steps that help doctors in their evaluation:
- Appearance of skin lesions, typically red and inflamed, often featuring pustules
- Patient history including previous skin conditions or irritations
- Symptomatology such as itching, tenderness, or burning sensations
- Location of the lesions, which can include any hairy area of the body
To choose the right ICD-10 code, using the correct diagnosis criteria is important. Seeing how the folliculitis diagnosis code affects billing shows why accurate documentation is a must.
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Skin Lesion Appearance | Red, inflamed areas often with pustules |
| Patient History | Previous skin conditions, irritations, or follicular involvement |
| Symptoms | Itching, tenderness, or burning sensations associated with lesions |
| Location | Commonly found in areas with hair follicles, e.g., scalp, beard, arms |
Using the folliculitis diagnosis code right, based on these points, makes treatment and billing smoother. It cuts down on claims being denied because of missing or wrong documentation.
Common Treatments for Folliculitis
Managing folliculitis well often means a plan that fits the cause. With various types to deal with, doctors must pick the right folliculitis treatments. Here, we look at two main kinds of treatment.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments help with mild to moderate folliculitis. They can include:
- Antiseptic cleansers to lower skin bacteria
- Antifungal shampoos against fungus like Malassezia
- Topical antibiotics, such as mupirocin or clindamycin, for bacterial folliculitis
When dealing with folliculitis from hot tubs, staying clean is key. For tough cases, doctors may use systemic antifungal drugs.
Oral Medications
If topical treatments don’t work, doctors may go for oral meds. These include:
- Antibiotics, like cephalexin or dicloxacillin, for severe bacterial folliculitis
- Oral antivirals such as acyclovir for viral folliculitis from herpes simplex
- Systemic antifungal medicines, like itraconazole, for pityrosporum folliculitis
Choosing the best treatment, be it topical or oral, helps patients get better quickly and lowers complication risks.
Understanding ICD-10 Code for Folliculitis Infection
Folliculitis is a skin issue caused by bacterial infections. The main culprit is Staphylococcus aureus. Healthcare workers need to know the ICD-10 code for folliculitis, L73.9. This code is vital for getting the treatment costs covered.
Clinicians must tell apart superficial from deep folliculitis. Superficial types show up as red bumps and are easier to treat. But deep folliculitis can get serious, causing cellulitis, especially in those with diabetes. In serious cases, about 30% can turn into worse infections needing stronger treatments.
Risk factors for folliculitis include bad hygiene and using hot tubs, causing up to 15% of cases. Knowing the patient’s history is important for treatment, especially since some types of scalp folliculitis come back in about 25% of cases.
If you’re looking for more information, check out understanding folliculitis infection for better management and coding tips. Here’s a quick list of ICD-10 codes related to folliculitis:
| ICD-10 Code | Description | Billable Status |
|---|---|---|
| L73.9 | Follicular disorder, unspecified | Billable |
| L66.4 | Folliculitis ulerythematosa reticulata | Billable |
| L72.12 | Pilonidal cyst | Non-billable |
| L72.2 | Follicular cyst of skin | Non-billable |
| L72.3 | Steatocystoma | Non-billable |
| L72.8 | Other epithelial cysts | Non-billable |
Navigating ICD-10 Folliculitis Unspecified
In the world of medical billing, knowing how to use the icd 10 folliculitis unspecified code is key. This is especially true when symptoms don’t match a certain type of folliculitis. Using code like L73.9 allows doctors to document correctly and take care of their patients. This guide talks about when to use this code and important coding rules.
When to Use this Code
Doctors should use the icd 10 folliculitis unspecified code when symptoms are unclear. This includes several situations:
- When symptoms appear but there’s no known cause or pattern.
- If a patient has many symptoms of a follicle issue but no confirmed diagnosis.
- When more tests need to be done or results are not clear.
It’s crucial to code correctly based on the coding guidelines. Proper coding helps with insurance claims and makes sure patients’ records are accurate.
ICD-10 Code for Superficial Folliculitis
The icd 10 code for superficial folliculitis is key for experts handling skin infections. It specifically uses the billable code “Perifolliculitis capitis abscedens,” marked as L66.3. This code started on October 1, 2024. It’s part of the L00-L99 range, which deals with skin and underneath skin diseases.
This code, L66.3, is considered a minor skin disorder. It’s linked to two main Diagnostic Related Groups (DRGs): MS-DRG 606 and MS-DRG 607. The first includes minor skin disorders with major issues or other health problems. The second group covers minor skin disorders without these complications.
Another code, L73.9, also talks about superficial folliculitis but more generally, as an unspecified follicular disorder. This shows how critical precise coding is for right treatment and payment. Notably, the L66.3 code has remained the same since the ICD-10-CM rolled out in 2015, keeping billing consistent until 2024.
| ICD-10 Code | Description | Effective Date | DRGs |
|---|---|---|---|
| L66.3 | Perifolliculitis capitis abscedens | October 1, 2024 | 606, 607 |
| L73.9 | Superficial folliculitis, unspecified | October 1, 2015 | 606, 607 |
For successful handling of skin infections, it’s crucial for health workers to know how to bill and code properly. Recognizing the icd 10 code for superficial folliculitis helps ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment notes.
ICD-10 Code for Deep Folliculitis
The code L66.4 is key for diagnosing deep folliculitis. It’s been in use since October 1, 2015. This code is part of a range for skin and under-skin diseases, marked as L00-L99. Knowing how deep the folliculitis is lets doctors plan the best treatment.
Differentiating Between Superficial and Deep Folliculitis
It’s important to tell the difference between superficial and deep folliculitis. Deep folliculitis symptoms include:
- Painful nodules beneath the skin surface
- General swelling and redness
- Possible pus-filled lesions
Superficial folliculitis looks like small red bumps on the hair follicle’s surface. Deep folliculitis can lead to scarring or more infections. Knowing the difference affects how doctors treat and bill for these conditions.
| Characteristic | Superficial Folliculitis | Deep Folliculitis |
|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Red bumps or pustules on the skin | Painful nodules, swelling, pus-filled lesions |
| Potential Complications | Rarely leads to serious issues | May cause scarring or secondary infections |
| ICD-10 Code | L66.0 (Superficial) | L66.4 (Deep) |
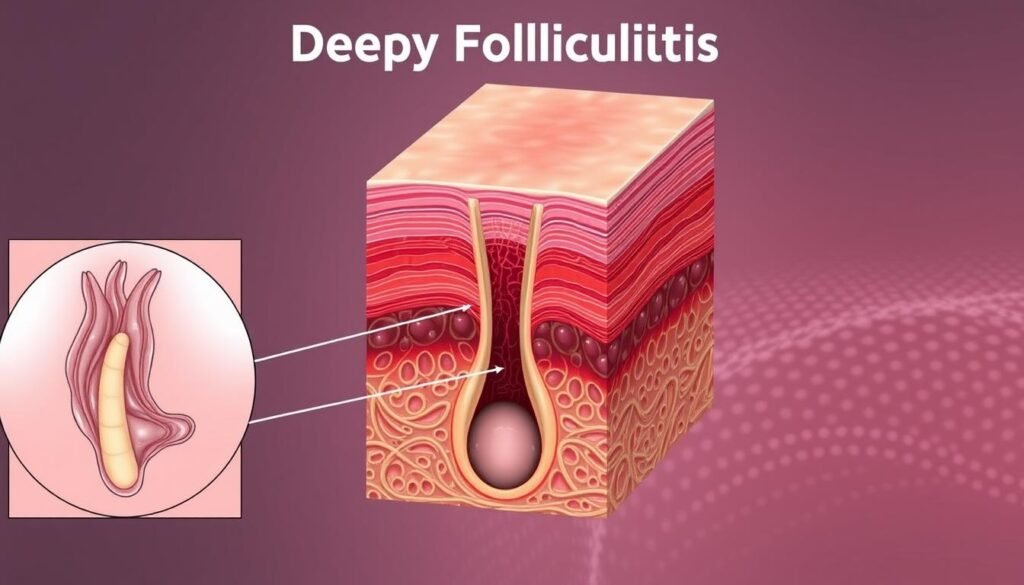
Understanding the different types of folliculitis helps medical workers. Correct coding improves patient care and billing.
Importance of Coding in Medical Billing
In healthcare’s changing world, coding’s role is critical. It ensures accurate medical billing, affecting reimbursement and record accuracy. Correct ICD-10 coding is crucial to prevent billing issues for healthcare providers.
The Role of Accurate Coding in Reimbursement
Correct coding is key to getting paid. Claims with wrong ICD-10-CM codes often get denied, as per the Social Security Act’s rules. About 25% of claims to Part A MAC fail due to coding errors. Healthcare places need correct codes on every claim to show the patient’s true condition and cut these risks.
Some services need special codes, like -GA or -GX, if they’re not covered. For example, -GA is used if Medicare might not pay, and the patient signs an Advance Beneficiary Notice (ABN). Since April 1, 2010, claims with -GA without an ABN get denied. This shows how vital the right codes are.
It’s also important to document why each procedure is done. Wrong coding of procedures like benign lesion removal can cause 5% to 20% of claims to be denied. Hospitals with good ICD-10 training for their staff see fewer mistakes and faster payments.
Hospitals using electronic records do better in coding than those with paper. Even so, continuous training is a must because many healthcare workers struggle with coding updates. About 40% don’t know the latest changes after their first training. Addressing these gaps ensures both good patient care and the financial well-being of healthcare places.
| Key Aspects | Impact of Accurate Coding |
|---|---|
| Claims Denial | 25% of claims denied due to incorrect coding |
| Modifier Requirement | Necessary to indicate non-coverage (e.g., -GA) |
| Documentation | Support rationale for procedures to reduce denials |
| Training Programs | 30% reduction in errors with comprehensive training |
| EHR Systems | 15% increase in coding accuracy compared to paper |
Conclusion
Wrapping up the talk about ICD-10 folliculitis, it’s clear how vital staying current with coding details is. For healthcare experts, knowing the ins and outs of Malassezia folliculitis (MF) is key. This knowledge leads to better diagnosis, improving patient care and the results of treatments. The summary also underlines noticing the different symptoms and treatments of this condition.
Coders have to work carefully to use the right ICD-10 codes. This avoids wrong diagnoses and ensures they get proper payment. Studies have pointed out that MF can impact many ages and body areas. This shows why coders need ongoing training in how to use codes correctly. Tools like dermoscopy help doctors tell MF apart from similar issues, which avoids billing mistakes.
Accurate coding helps in making the billing smoother and brings better outcomes for patients. There are further resources out there, like studies on diagnosis and treatment responses, offering deep insights for those interested. For deeper knowledge, clinical studies provide a wealth of information. Readers might find more helpful details in this detailed analysis.
