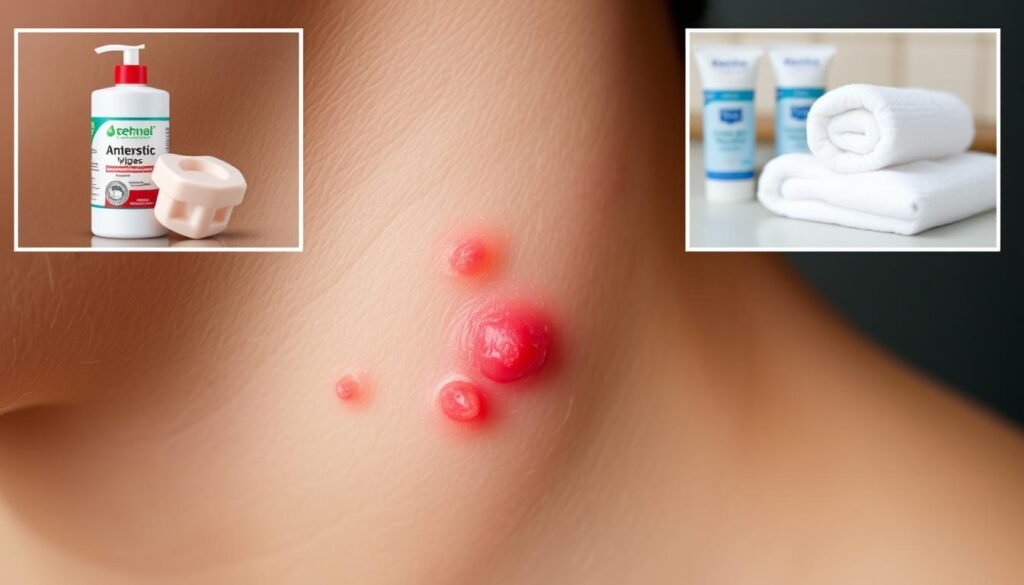
Folliculitis is not usually contagious, but certain kinds can spread in some situations. It’s a common skin issue that looks like red, swollen bumps, similar to acne. Many things, like certain medicines or health problems, can cause it. Knowing if it can spread is key for stopping and treating it effectively. If you want to learn how to prevent folliculitis, check this Mayo Clinic link.
Itchy bumps and skin irritation need attention to find the cause. It’s important to act early. This article will cover folliculitis signs, how it can spread, ways to treat it, and tips to keep your skin healthy.
Key Takeaways
- Folliculitis is often mistaken for acne due to its similar appearance and symptoms.
- Certain types, such as those caused by staph infections or herpes, can be contagious.
- Preventing folliculitis involves maintaining proper hygiene and avoiding tight clothing.
- Symptoms can include red bumps, pus-filled blisters, and itching.
- Understanding the various types of folliculitis can assist in appropriate treatment.
Understanding Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a skin issue where hair follicles get inflamed. It shows up as red, swollen bumps that may itch or hurt. Factors like bacterial infections, fungi, and irritation can cause it. Knowing the different kinds of folliculitis is key because they look different and have various causes.
Bacterial folliculitis is often caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Fungi like Malassezia are behind pityrosporum folliculitis. Sometimes, the herpes virus can trigger this skin problem too. It’s important to understand these types, as it shapes how we treat and manage them.
- Bacterial folliculitis is common, usually due to not keeping clean or skin contact.
- Fungal folliculitis happens in damp, warm places. Staying clean is key to avoiding it.
- Pseudofolliculitis barbae affects men with curly hair a lot and needs special care.
Not treating folliculitis can cause big problems, like scars or dangerous infections in the bloodstream. So, spotting and treating it early on is crucial for health and well-being.
What Causes Folliculitis?
Folliculitis often starts with an infection in the hair follicle. Staphylococcus aureus is the usual cause. Knowing the different folliculitis causes helps treat and manage it well.
Fungus can cause it too, leading to fungal folliculitis. Shaving, waxing, or tight clothes can inflame hair follicles. Also, skin irritation and blocked follicles can make it worse.
People with diabetes or those who shave a lot are more at risk. Steroids, acne, dermatitis, some medications, and irritant chemicals increase the chance of getting folliculitis.
Symptoms include itching and tender bumps on the skin. This often happens on the face, neck, and thighs. Some cases of folliculitis get better on their own, but sometimes treatment is needed.
Knowing these triggers helps spot the condition early. This means quicker treatment and relief.
| Type of Folliculitis | Common Causes | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Folliculitis | Staphylococcus aureus, shaving | Itching, tender bumps |
| Fungal Folliculitis | Heat, moisture | Pus-filled sores, inflamed skin |
| Pseudofolliculitis Barbae | Curly hair ingrowth during shaving | Painful bumps, inflammation |
| Pityrosporum Folliculitis | Yeast overgrowth | Itchy, reddish bumps |
Signs and Symptoms of Folliculitis
Folliculitis shows up with different folliculitis symptoms that impact the skin and comfort. It starts with small, red bumps or blisters filled with pus near hair follicles. These spots might feel tender and often cause itchy skin.
People suffering from this issue might feel a burning feeling, making the discomfort worse. Spotting the signs of folliculitis early leads to better control of the situation. It’s crucial to observe these symptoms to know when to seek treatment. Without treatment, the problem could get much worse.
Taking steps early on to care for your skin can help ease itchy skin and stop folliculitis from getting worse. Keeping skin clean and steering clear of things that can irritate it are key. For more tips on dealing with this skin problem, check out this resource.
| Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Red Bumps | Small, elevated, and inflamed lesions around hair follicles |
| Pus-filled Blisters | Blisters that may develop as a result of infection |
| Itching | Intense itching sensations leading to discomfort |
| Tenderness | Softness and sensitivity in the affected regions |
| Burning Sensation | Feelings of inflammation and heat in the skin |
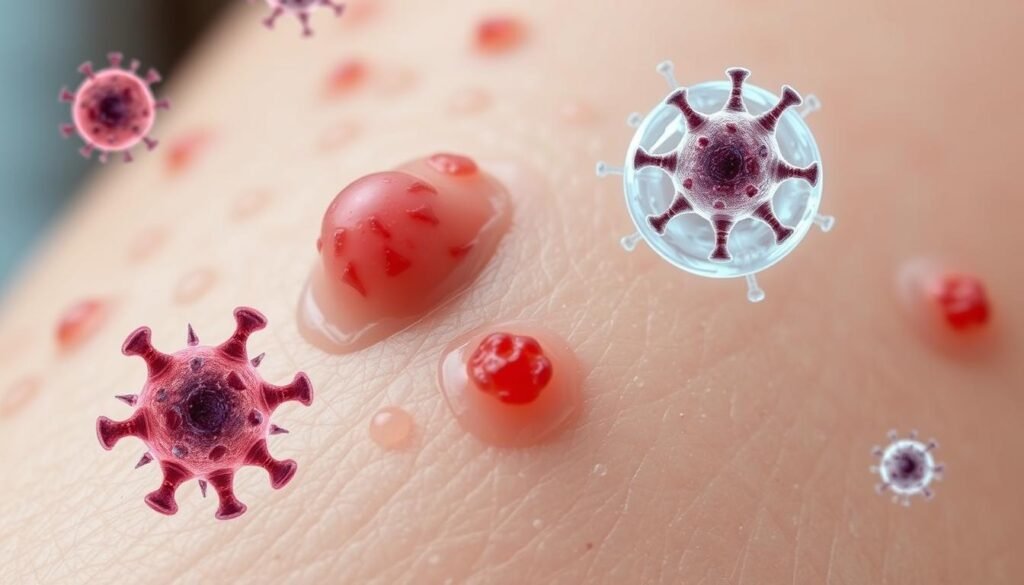
Can Folliculitis Spread?
It’s important to know if folliculitis can spread to manage and prevent it well. Some types have limited contagiousness, but others can spread under certain conditions. By understanding how it spreads, we can better protect ourselves and others.
Types of Folliculitis That Are Contagious
Some folliculitis types spread through bacterial infections. Staphylococcus aureus is a common cause. It spreads through skin contact or using someone else’s items like razors or towels. Hot tub folliculitis comes from Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria in badly kept pools or hot tubs. Also, yeast can cause pityrosporum folliculitis by entering the hair follicles. These examples show how folliculitis can move from person to person.
How Folliculitis Can Spread
How can folliculitis spread? Here are some common ways:
- Close skin-to-skin contact, especially during intimate moments.
- Using shared items such as towels, clothes, or razors.
- Being in contaminated water in pools or hot tubs not well kept.
People in moist places like gyms or shared showers need to be careful. Steps like good hygiene, showering after using a pool, and wearing clothes that let skin breathe help a lot. It’s also vital to keep hot tubs clean to stop folliculitis transmission. By doing these things, we can keep both ourselves and others safe.
| Type of Folliculitis | Contagious? | Transmission Method |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Folliculitis | Yes | Skin contact, sharing personal items |
| Hot Tub Folliculitis | Yes | Contaminated water |
| Pityrosporum Folliculitis | Yes | Skin contact, environmental exposure |
| Gram-Negative Folliculitis | Yes | Ignores hygiene or prolonged antibiotic use |
Bacterial Folliculitis: An Overview
Bacterial folliculitis is a skin issue where hair follicles get inflamed. It’s often due to staph bacteria. People of any age can get it, especially on the beard, arms, back, buttocks, and legs. Spotting the symptoms early helps treat and ease them.
Causes of Bacterial Folliculitis
A staph infection usually causes bacterial folliculitis. It happens when bacteria enter hair follicles. This can occur through shaving or tight clothes. Several factors can raise the risk of getting it:
- Warm, moist places, like badly kept hot tubs.
- Using shared items like towels or razors.
- Skin issues caused by makeup or oils.
- Weak immune systems from conditions like diabetes or HIV.
Symptoms and Treatment
Bacterial folliculitis shows up as red, inflamed bumps. These may fill with pus and get crusty if touched. They can feel itchy or sore. Mild cases might heal in two weeks. But, getting the right folliculitis treatment is key for quick recovery. Treatment options often include:
- Topical antibiotic lotions or gels for light infections.
- Oral antibiotics for tougher or returning cases.
- Over-the-counter creams to soothe itchy skin.
- Cleaning the area daily with antibacterial soap.
- Using warm, moist compresses to drain affected follicles.
With proper treatment, bacterial folliculitis usually gets better. Yet, it’s important to know it can come back or spread. Taking care of your skin is vital for staying healthy.
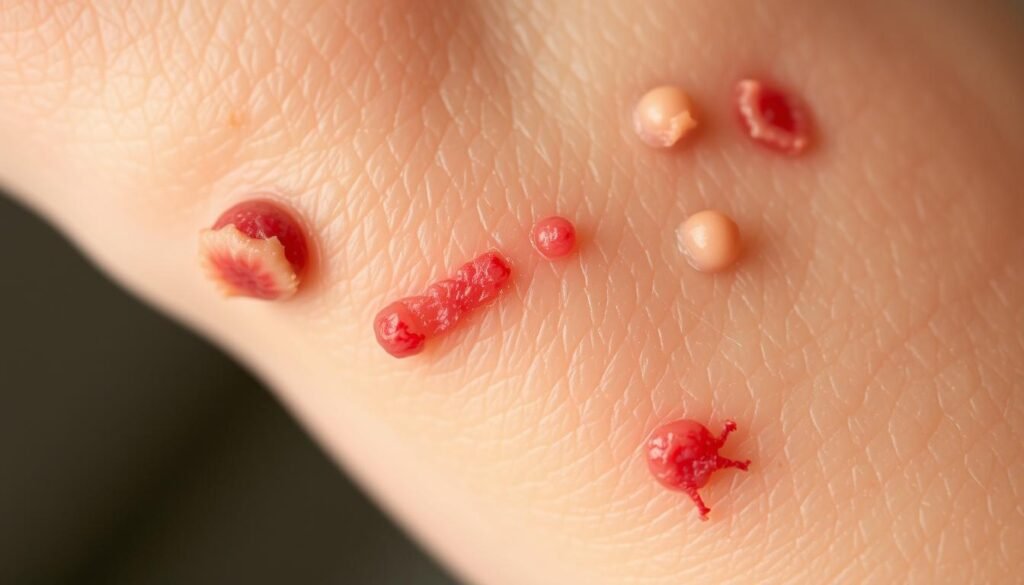
Fungal Folliculitis: What to Know
Fungal folliculitis is often due to a *yeast infection* known as pityrosporum folliculitis. It shows as itchy, pus-filled bumps mostly on the back and chest. People with it feel a lot of itching.
This condition can turn into a long-lasting problem, needing good management. Treatment often includes antifungal meds from doctors, to help control and ease symptoms. Without the right care, *fungal folliculitis* can keep coming back.
Knowing the symptoms and traits of pityrosporum folliculitis is key. Spotting the itchiness and unique bumps can make life much better. Regular check-ups with doctors are important to find treatments and prevent future outbreaks.
Hot Tub Folliculitis: A Common Concern
Hot tub folliculitis is known in the medical world as pseudomonas folliculitis. It comes from being in hot tubs or pools that aren’t well taken care of. The culprit is a bacterium called Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which loves warm, untreated water. People usually see symptoms like itchy, red bumps after using such waters.
Folks might also feel feverish, tired, have a sore throat, headaches, and swollen glands. Sometimes, they could feel nauseous too. Children and those with weaker immune systems need to be extra careful. Usually, this rash gets better on its own in 7-10 days. But if it doesn’t improve, seeing a doctor is a good idea.
To prevent hot tub folliculitis, keeping swimming areas clean is key. It’s important to check water quality often and make sure there’s enough chlorine. Showering right after being in a hot tub helps, as does changing out of wet clothes. If you spot early signs, getting advice from a doctor can help manage the condition.
| Symptoms of Hot Tub Folliculitis | Description |
|---|---|
| Red, itchy bumps | Common initial indication of infection |
| Pus-filled bumps | May develop within infected areas |
| Fever | Possible systemic reaction to infection |
| Fatigue | General feeling of tiredness |
| Sore throat | Could accompany other symptoms |
| Swollen lymph nodes | Indication of an immune response |
| Nausea | Might occur in some cases |
Preventing Folliculitis: Effective Tips
Folliculitis prevention is key to keeping skin healthy. Proper skin care and smart clothing choices can lower the risk of getting it.
Daily Skin Care Practices
Good skin care routines are vital to avoid folliculitis. It’s crucial to wash regularly with a gentle cleanser. This removes dirt and germs.
Using clean towels after showering can stop bacteria from reaching the skin. Applying moisturizers helps with dryness and keeps the skin’s barrier strong. Aloe vera gel might help fight certain bacteria, so it’s good for skin care.
Shaving gently prevents harming hair follicles. This is worth considering to keep skin smooth and clear.
Choosing the Right Clothing
What you wear greatly affects folliculitis risk. Loose clothes reduce skin friction and irritation.
Selecting garments made of breathable fabrics helps avoid sweat and heat. This can prevent the condition from getting worse. Ensure socks and gloves fit well but are not too tight to prevent friction.
Wearing clothes that aren’t too tight protects areas likely to get folliculitis. For more on managing this condition, check out folliculitis treatment and prevention.
Folliculitis Treatment Options
Folliculitis is a skin issue that people of all ages get. It looks like red spots around hair roots. For mild cases, home remedies like warm cloths and antibacterial soaps help a lot. Keep clean and use kind skin products at home.
If the problem is big or doesn’t go away, see a doctor. A doctor might suggest medicines you put on your skin or pills, depending on the folliculitis. For really bad cases, you might need stronger medicine or even a small surgery to get better.
To avoid folliculitis, shave the right way, wear comfy clothes, and keep your skin clean and dry, especially when it’s hot. Knowing your symptoms helps you fight folliculitis better. By taking these steps, you can help stop it before it starts.
Combining home care with doctor’s advice is key to better skin. It’s important to know your treatment options and get help when needed.
Folliculitis vs. Acne: Key Differences
It’s essential to know the differences between folliculitis and acne to treat them right. While they may look alike, their causes aren’t the same. Folliculitis starts from infections in hair follicles, showing up as red, inflamed bumps that may have pus. Acne, however, comes from blocked pores due to too much sebum and dead skin cells, leading to whiteheads and blackheads.
Folliculitis can affect anyone, but those who shave often or use hot tubs may get it more. If it gets severe, it can cause permanent hair loss and scars. This highlights why catching it early and treating it properly is crucial. Acne affects about 85% of people at some point, and it’s mostly due to genetics.
When comparing both skin issues, prevention stands out as key. For acne, sticking to a regular skin care routine helps a lot. People prone to folliculitis should avoid staying sweaty and use specific products like benzoyl peroxide to lower infection chances. Knowing the differences helps in choosing the right treatment method.
| Aspect | Folliculitis | Acne |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Infection of hair follicles | Clogged pores from excess sebum |
| Appearance | Red, inflamed bumps, often filled with pus | Whiteheads, blackheads, and cysts |
| Common Locations | Areas with hair growth, such as face and legs | Face, chest, and back |
| Prevalence | Affects individuals of all ages; common in shavers | Affects approximately 85% of people at some point |
| Treatment Methods | Topical antibacterial washes, antifungal treatments | Skincare routines, over-the-counter medications |

Conclusion
It’s vital to understand folliculitis to keep your skin healthy. This condition, which includes bacterial and fungal types, requires attention. Knowing about it helps in identifying symptoms early and starting treatments quickly.
This condition can spread, making it important to know. The culprit is often the Staphylococcus aureus germ.
To prevent folliculitis, practice good hygiene. Use the right shaving techniques. Be careful in places with communal water.
These steps can lower your chances of getting folliculitis. They protect your skin. Knowing about folliculitis lets you take charge of your skincare.
Spotting signs and taking action is key for healthy skin. This proactive approach prevents new outbreaks. Everyone can enjoy clearer, healthier skin by doing so.