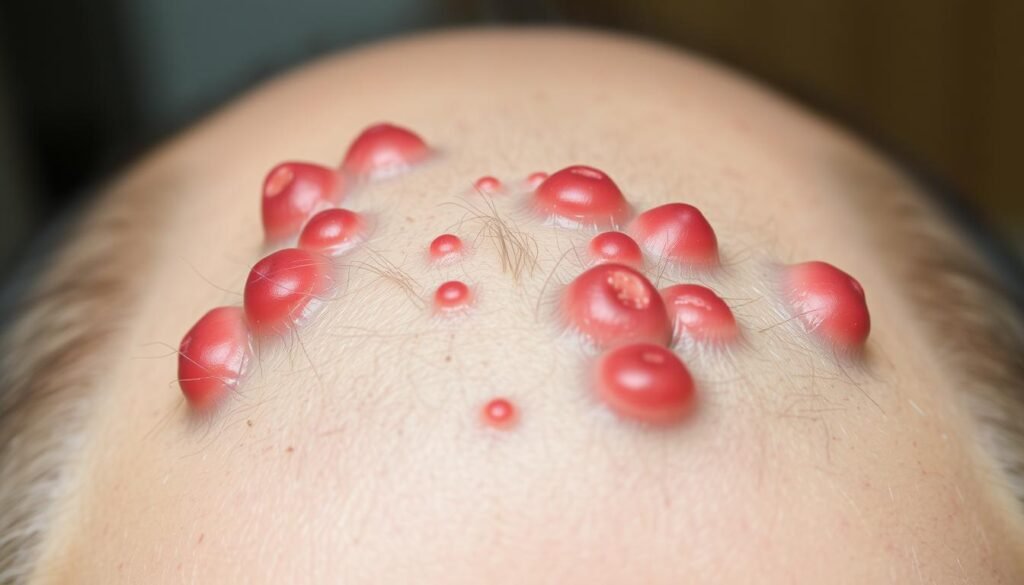
Bacterial folliculitis, mostly caused by Staphylococcus aureus, is quite common. It affects hair follicles, leading to itchy rashes, similar to scalp acne from inflamed hair follicles. Though these bumps are usually not contagious, knowing how to treat and prevent them is key to keeping your skin healthy.
This piece aims to delve into hair follicle inflammation and its treatments. It will cover how to identify symptoms and know when to seek medical help. This will equip readers with the knowledge to tackle this skin issue that could cause discomfort or even permanent damage if ignored.
Key Takeaways
- Folliculitis bumps on the scalp commonly come from bacterial infections and affect many people.
- The symptoms can look a lot like scalp acne, with itchy, pus-filled bumps indicating inflammation.
- Most cases are treatable at home using warm compresses and antibacterial soaps.
- It’s crucial to act quickly to avoid problems like scarring and hair loss.
- Knowing what increases your risk can help prevent scalp folliculitis in the future.
Understanding Folliculitis
Folliculitis is when hair follicles get inflamed. It can happen anywhere on the body with hair, including the scalp. This issue causes red, painful bumps that look like a mild rash. It’s key to know about folliculitis to identify symptoms and find the right treatment.
Folliculitis comes in two forms: non-infective and infective. Non-infective types happen from shaving, sweating a lot, or certain meds, like corticosteroids. On the other hand, infective folliculitis occurs because of bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa are common causes.
Folliculitis symptoms are usually small, red bumps with a hair in the middle. Recognizing these signs is helpful to tell it apart from other skin issues. Sometimes, it can be chronic, especially in areas like the beard. Darker-skinned men with curly hair may have ongoing inflammation.
Bacterial folliculitis is often due to broken skin barriers. This lets bacteria enter the hair follicles. Wearing tight clothes, a lot of skin contact, and a weak immune system increase the risk. To prevent it, stay clean, keep your skin dry, and wear loose clothes.
In short, folliculitis is common but manageable. Knowing its symptoms lets you seek treatment early. Plus, taking steps to avoid it can make a big difference.
What Are Folliculitis Bumps on Scalp?
Folliculitis bumps on the scalp are tiny, red, inflamed bumps around hair follicles. They can be tender, itchy, and may have pus inside. If not treated, they can turn into crusty sores, increasing discomfort and infection risk.
These bumps usually first appear near the hairline. They may spread across the scalp. The condition can affect the skin’s look and harm hair follicles. Severe cases can cause more pain and complications.
There are many types of folliculitis. Bacterial folliculitis is caused by bacterial infections. Others may result from ingrown hairs or certain hair care habits. Recognizing symptoms early is key for the right treatment. For more info on symptoms, visit this resource.
Knowing about these bumps can help prevent them. It also helps plan how to stop further problems.
Symptoms of Scalp Folliculitis
Scalp folliculitis symptoms include itchy, painful bumps on the scalp. People might see pus-filled blisters that cluster. This often leads to a lot of discomfort. When the condition gets worse, yellowish-brown scabs show up. These scabs hint at irritation or an infection.
Along with these symptoms, you may feel a burning pain. It’s important to spot these signs early for quick treatment. Quick action helps avoid serious problems like scars or losing hair. If you see these signs, watch your scalp closely.
Common Causes of Scalp Folliculitis
Scalp folliculitis comes from different sources, mainly bacteria, fungi, and hair follicle irritation. The biggest cause is Staphylococcus aureus, leading to infection. Those with damaged follicles from scratching, tight styles, or shaving face higher risks.
Other key causes include:
- Wearing hats or helmets in hot weather
- Too much hair product use causing scalp irritation
- Issues like acne or dermatitis affecting skin
- Excess sebum production clogging hair follicles
People who sweat a lot, have diabetes, or weakened immune systems may face more danger. Pityrosporum folliculitis, a fungal issue, is treated with oral antifungal drugs. Keeping the scalp clean and using special shampoos can control scalp folliculitis.
Knowing these causes helps in finding good prevention and treatment methods. Recognizing personal risk factors allows for better scalp care and lowers infection chances.
Risk Factors for Developing Folliculitis
Understanding the risk factors for folliculitis is vital. It helps individuals take steps to lower their chances of getting it. Certain lifestyles and health issues make some people more prone to it. Key risks include having diabetes, using antibiotics for a long time, and shaving often.
Men with coarse hair are at higher risk. Their hair may grow back into the skin or irritate it. Having a weak immune system, due to HIV or cancer, also raises the risk. Tight clothes and spending time in hot tubs that aren’t clean increase the chance of getting scalp folliculitis.
Conditions like acne and dermatitis can make folliculitis more likely. Using dirty swimming pools or hot tubs can expose the skin to harmful bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus. Knowing these risks can guide better hygiene and skincare choices.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Coarse Hair | Hair texture that is more likely to cause ingrown hairs and irritation. |
| Weakened Immune System | Conditions like HIV or certain cancers can increase susceptibility to infections. |
| Long-Term Antibiotic Use | Regular use may alter skin flora, leading to imbalance and risk of infection. |
| Frequent Shaving | Can cause skin irritation and open pores to bacteria. |
| Unclean Hot Tubs | Exposure to contaminated water can introduce harmful bacteria. |
| Skin Conditions | Conditions such as acne or dermatitis can lead to occluded follicles. |
How to Treat Mild Cases of Folliculitis at Home
Mild folliculitis can usually be treated at home with easy remedies. Knowing the best methods can speed up relief and stop the condition from getting worse. Try these simple steps.
Warm Compresses for Relief
Warm compresses can ease discomfort quickly. They help drain pus and calm irritation. It’s best to apply a warm, damp cloth to the sore area three to six times a day.
This regular treatment can lessen swelling and aid healing.
Using Antibacterial Soap
Good hygiene is key for treating mild folliculitis. Use antibacterial soap to get rid of harmful bacteria. Pay extra attention to cleaning areas like the hairline where bacteria gather.
Washing regularly with antibacterial soap can prevent more outbreaks.
Antidandruff Shampoo with Antifungal Properties
Using an antifungal shampoo, made for dandruff, helps against folliculitis. These shampoos fight fungus and inflammation. They keep hair follicles clean, lowering the chance of it coming back.
Pairing this with other treatments boosts your chances of managing mild cases well.
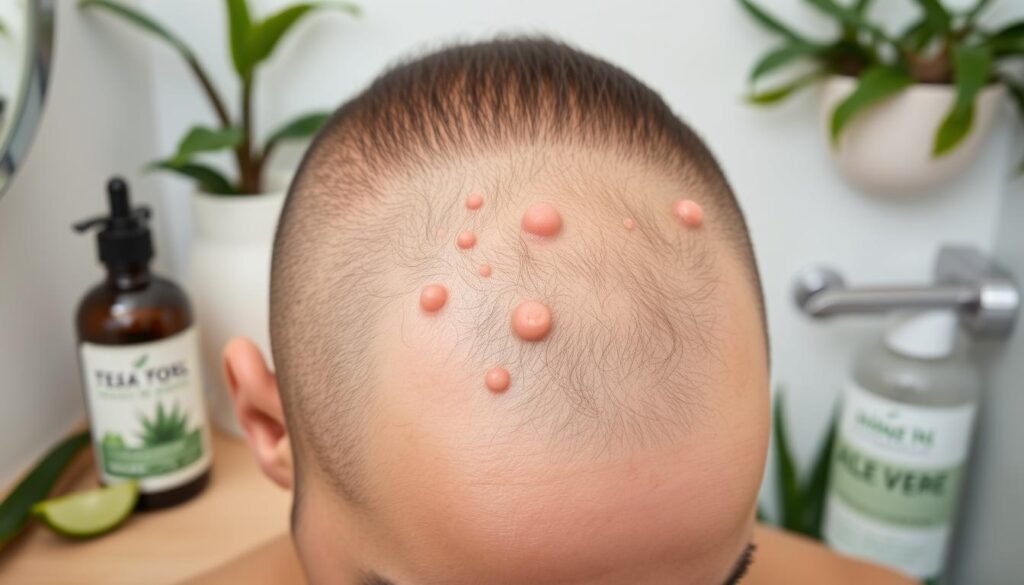
Over-the-Counter Treatments for Severe Cases
When you have severe folliculitis, over-the-counter remedies can really help. People often use antibiotic ointments, like Neosporin, for bacterial infections from this condition. These creams help lessen swelling and stop infections from spreading.
Along with these ointments, antifungal shampoos also do a lot of good. They’re made to kill the yeast that causes folliculitis, leading to healthier skin and scalp. Creams like OTC hydrocortisone are great for reducing itching and irritation. These make dealing with symptoms a lot easier.
To boost these treatments, try some self-care. Warm, damp cloths on the irritated areas soothe the skin. If things don’t get better, seeing a doctor is a smart move. Serious cases might need extra care. For tips on handling mild cases at home, check out this guide.
| Treatment Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic Ointments | Topical treatments for bacterial folliculitis | Neosporin |
| Medicated Shampoos | Shampoos designed to combat fungal infections | Ketoconazole, Selenium sulfide |
| Corticosteroid Creams | Anti-inflammatory creams to ease itching and swelling | Hydrocortisone cream |
| Warm Compresses | Soothing moist cloths applied to reduce irritation | Washcloth soaked in warm water |
These over-the-counter options are key in fighting severe folliculitis. Yet, getting advice from a doctor can often make treatment even more effective, especially in complicated cases.
When to See a Doctor for Folliculitis
If your symptoms of folliculitis don’t get better with home care or get worse quickly, it’s vital to see a doctor for folliculitis. Signs like pus-filled blisters, fever, a lot of pain, or swelling mean you might need medical help. These symptoms could show a more serious infection.
Keep a close eye on your condition. If folliculitis spreads or still hurts, go see a doctor. They can check you out and might do tests to find the cause, like spotting certain bacteria or fungi.
Folliculitis usually gets better with treatment. But, if it keeps coming back or doesn’t improve at first, talking to a doctor is important. They might prescribe creams or pills to fight bacteria or fungus or suggest other treatments to help you heal and stop more problems.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Folliculitis
Taking proactive steps can help a lot in avoiding folliculitis. It’s key to focus on scalp hygiene. Cleaning your scalp often can fight off bacteria, lowering your risk of getting folliculitis. It is wise to wash your scalp after being active to get rid of sweat and dirt that might irritate your skin.
Not wearing tight hats is also crucial for prevention. Such hats can rub your skin and clog your hair follicles, which might lead to infection. Choosing hats that fit loosely or letting your scalp breath can reduce this risk.
It’s also vital not to share personal items like combs and hats. Since you can catch folliculitis through direct contact with infected objects, using your own things is a good preventive step. This practice is key to never getting folliculitis.
If you get ingrown hairs often, shaving the right way is very important. Gentle shaving and proper skin care can lower the chance of ingrown hairs. Keeping your skin hydrated and moisturized also supports a healthy scalp, which helps in preventing folliculitis.
| Preventive Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Maintain Scalp Hygiene | Regularly wash the scalp to remove sweat and bacteria. |
| Avoid Tight Hats | Choose looser hats to prevent friction and blockage of hair follicles. |
| Use Personal Items | Avoid sharing combs and hats to decrease transmission risks. |
| Gentle Shaving | Utilize proper techniques and exfoliation to prevent ingrown hairs. |
| Stay Hydrated | Keeping skin moisturized helps improve overall scalp health. |
Conclusion
Keeping a healthy scalp means managing folliculitis well. This condition leads to symptoms like red bumps and itching. It’s often due to infections. Spotting these signs early helps get the right treatment, stopping the condition from getting worse.
For mild cases, it’s key to use warm compresses and medicated shampoos. But if the problem doesn’t go away or gets really bad, seeing a doctor is important. They can check your symptoms and create a treatment plan just for you. Keeping your scalp clean and avoiding things that trigger folliculitis are big steps towards good scalp health.
Knowing what causes folliculitis and how to treat it can make life better. Taking care of your scalp and getting help when needed helps control the condition. This way, you can feel better every day.