Scalp folliculitis is a problem that affects people at any age, from babies to the elderly. It is mainly caused by mild bacterial infections. This leads to inflamed hair follicles, making the scalp uncomfortable and creating unsightly bumps. Fortunately, there are solutions like antibiotic creams and gels.
These treatments are key to battling this widespread issue. By knowing when and how to use them, you can greatly improve the health of your scalp. This also helps soothe the symptoms that come with folliculitis.
Key Takeaways
- Topical antibiotics are often prescribed for mild bacterial infections related to scalp folliculitis.
- Oral antibiotics are generally reserved for severe or recurrent cases.
- Antifungal treatments are suggested for fungal infections rather than bacterial infections.
- Good self-care practices can effectively manage mild symptoms at home.
- Consulting a healthcare professional can ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Scalp Folliculitis
Scalp folliculitis is a skin issue where hair follicles get inflamed. It’s mainly due to bacterial infections, like those by Staphylococcus aureus. People with this issue may face discomfort that affects their life quality.
What is Folliculitis?
Folliculitis is an infection in the hair follicles. It can happen anywhere on the body, scalp included. It often comes from bacteria. Knowing about folliculitis is key to spotting symptoms and starting the right treatment.
Common Symptoms of Scalp Folliculitis
The signs of scalp folliculitis include:
- Itchy or painful bumps on the scalp
- Pus-filled blisters that can pop
- Redness and swelling on the scalp
- Scalp feeling sore or uncomfortable
These symptoms can be mild or severe and might look like other skin issues. So, recognizing them is important for managing them well. For more info on symptoms and treatments, check out this resource.
Types of Folliculitis
Folliculitis has different types based on the cause:
| Type of Folliculitis | Cause | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Folliculitis | Staphylococcus aureus | Often itchy with pus bumps. |
| Gram-negative Folliculitis | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Comes from dirty water, like after using a hot tub. |
| Fungal Folliculitis | Malassezia furfur | Usual in teens, shows as bumps on upper body. |
| Viral Folliculitis | Herpes virus | Has blisters clusters on the scalp. |
| Demodex Folliculitis | Demodex folliculorum mite | Seen in oily areas; linked to immune problems. |
| Eosinophilic Folliculitis | Immune dysregulation | Rare, mostly in advanced HIV cases. |
Identifying the type of folliculitis helps pick the best treatment. For advice on topical treatments, visit this link.
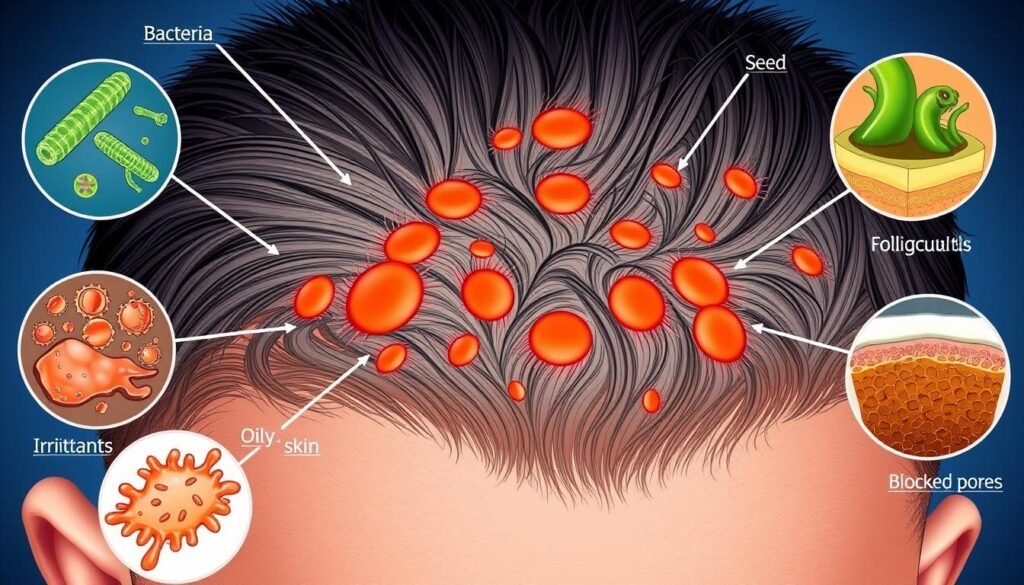
Causes of Scalp Folliculitis
Understanding what causes folliculitis gives us clues on how it happens. It’s a common skin issue, involving many factors. Bacterial infections are a major player.
Bacterial Causes
Mostly, Staphylococcus aureus, a germ, causes bacterial folliculitis. It’s harmless on our skin until it enters hair follicles. Another cause is Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This leads to hot tub folliculitis from poorly chlorinated water.
Other Contributing Factors
Other things can also increase the risk of getting folliculitis. These include:
- Perspiration
- Irritation from tight clothing
- Poor hygiene practices
Each of these factors can make you more prone to this condition. People with skin issues, weak immune systems, or doing hair removal may be at higher risk. It can affect anyone, from babies to the elderly. Knowing these causes can help prevent it and manage symptoms better.
Diagnosis of Scalp Folliculitis
A healthcare provider starts the diagnosis with a careful skin check. They look closely at the skin, asking about symptoms and health history. Knowing the patient’s past health can give hints on what caused the infection.
Visual Examination by a Healthcare Provider
First, a visual exam is done to spot signs of folliculitis. This includes checking for redness, swelling, and pus-filled bumps. It’s important to see if the signs match bacterial or fungal infections to choose the right treatment.
Testing and Culturing for Bacteria
If it seems like a bacterial infection, more tests may be needed. Getting a sample of the bacteria can show what’s causing the problem. It’s key in figuring out if certain bacteria, like Staphylococcus aureus or Pseudomonas aeruginosa, are to blame. Sometimes, getting a skin sample or doing biopsies is needed for a clear diagnosis.
Importance of Topical Antibiotics
Topical antibiotics are crucial for treating skin conditions like scalp folliculitis. They attack bacteria right where the infection is. This stops the bacteria from growing, which helps the skin heal faster. It also lowers the chance of more serious problems. Knowing why topical antibiotics matter is key to successful treatment.
How Topical Antibiotics Work
Topical antibiotics stop bacteria by breaking their cell walls or stopping their growth. They tackle the bad bacteria causing issues like folliculitis. Drugs like clindamycin and mupirocin go after certain bacteria. This makes symptoms better and helps the skin heal. When used right, antibiotic ointment protects from more germs. It helps the skin heal itself. Using these ointments regularly keeps worse infections at bay.
Best Topical Antibiotics for Folliculitis
When it comes to fighting scalp folliculitis, some antibiotics stand out. Mupirocin works great against Staphylococcus aureus and is often chosen for its power. Clindamycin is good for tackling anaerobic bacteria that cause acne and worsen folliculitis. Benzoyl peroxide is not just for acne. It can also stop folliculitis because it fights a wide range of bacteria.
It’s important for skin care experts to know about different topical antibiotics. They should understand how these treatments work and their possible side effects. This knowledge helps pick the best treatment for each person. For a deeper look into how topical antibiotics are used in dermatology, check this literature review.
Other Treatment Options
There are many treatments for scalp folliculitis beyond standard ones. You can use both prescription and over-the-counter antibiotics based on how severe it is.
Prescription Topical Antibiotics
For tough cases, prescription antibiotics can really help. One such medication is mupirocin. It’s effective as cream or ointment and works well for conditions like impetigo.
It’s even suitable for kids who are 2 months to 16 years old. Knowing how much to apply is important. For example, one gram of cream can cover a specific area of skin. Mupirocin has also been effective against certain secondary infections.
Over-the-Counter Topical Antibiotics
Minor issues of scalp folliculitis can be tackled with over-the-counter antibiotics. Products with bacitracin, polymyxin B, and neomycin are good for small cuts. They also help prevent more serious infections like impetigo in less severe cases.
Even though these products are easy to get, talking to a doctor is key. Sometimes, you might need something stronger, especially if the first attempts don’t work.
| Type of Antibiotic | Formulation | Uses | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mupirocin | Ointment/Cream | Folliculitis, Impetigo | Effective as oral erythromycin, approved for children |
| Bacitracin | Ointment | Minor abrasions | Widely available over-the-counter |
| Polymyxin B | Ointment | Minor skin infections | May be combined with other antibiotics |
| Neomycin | Ointment | Minor abrasions | Higher risk of allergic sensitivity with prolonged use |

Treating scalp folliculitis well requires a mix of methods. Both prescription and over-the-counter antibiotics are vital for fighting off infections and helping the skin heal.
For more details, visit this source.
Self-Care Measures for Scalp Folliculitis
To manage scalp folliculitis well, taking care of yourself is key. Good personal hygiene can help lessen symptoms and aid healing.
Good Hygiene Practices
Good hygiene plays a big role in handling scalp folliculitis. Here’s what you should do:
- Gently cleanse the scalp with antibacterial shampoo to eliminate bacteria.
- Avoid using oily hair products that can clog hair follicles.
- Wash hair regularly to remove dirt and sweat.
- Avoid tight clothing around the scalp to minimize irritation.
- Do not share personal items such as hats or combs to reduce the risk of infection.
Following these tips can ease mild issues and stop further problems. They are essential for anyone with this scalp condition.
When to Seek Professional Help
Sometimes self-care isn’t enough for scalp problems. You should see a doctor if:
- Symptoms worsen or don’t get better after 2-3 days of care at home.
- You notice new symptoms like fever or more pain.
- The issue spreads beyond the scalp or causes a lot of discomforts.
Getting professional advice is crucial. It helps avoid worse issues like scarring or hair loss.
| Self-Care Action | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Gentle cleansing with antibacterial shampoo | Reduces bacterial load on the scalp |
| Avoiding oily hair products | Prevents clogging of hair follicles |
| Regular hair washing | Keeps the scalp clean and free of irritants |
| Wearing loose-fitting clothing | Minimizes scalp irritation |
| Consulting a healthcare provider | Ensures proper diagnosis and treatment plan |
When to Use Topical Antibiotics
Topical antibiotics are key for treating scalp folliculitis. It’s crucial to know when they’re helpful. This guidance helps decide when to use them and when to switch to prescription antibiotics.
Guidelines for Usage
For mild to moderate scalp folliculitis, clindamycin and erythromycin are often suggested. They fight inflammation and bacterial infections. Start using these antibiotics at the first sign of pain, redness, or swelling. If symptoms get worse or don’t improve, see a doctor.
Here are the important guidelines:
- Use topical antibiotics early on for folliculitis signs.
- If the condition worsens, it’s time to reassess.
- Follow the prescribed times and doses to avoid resistance.
Indicators for Switching to Prescription Medications
If using topical antibiotics doesn’t help or serious infection signs show up, consider prescription antibiotics. Look out for pus, bad swelling, or fever. A healthcare provider’s advice is vital then.
Sometimes, you might need prescription antibiotics for tough bacteria or if over-the-counter options fail. Always listen to a healthcare professional’s treatment suggestions.
For more info, check out resources on skin care and antibiotics. Visit the American Academy of Dermatology and Biotin Life for insights on topical treatments.
| Symptom Severity | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
| Mild Symptoms | Use over-the-counter topical antibiotics |
| Worsening Symptoms | Consult a healthcare provider for assessment |
| Signs of Infection | Consider switching to prescription antibiotics |
Potential Side Effects of Topical Antibiotics
Topical antibiotics help fight skin infections, but knowing their possible side effects is important. It helps manage reactions and make informed choices. Side effects range from mild to serious, so it’s wise to be cautious.
Common Side Effects
Common mild side effects include:
- Redness at the application site
- Burning or stinging sensations
- Itching and irritation
- Dryness or peeling skin
Usually, side effects go away as your skin gets used to the treatment. Some people may face severe reactions like balance issues, hearing problems, or folliculitis. Using these antibiotics too much might cause infections, slowing down the healing.
When to Consult a Doctor
Keep an eye on your skin and health while using these antibiotics. Consult a doctor if anything unusual happens. Though very rare, serious allergic reactions demand urgent care. Seek help if you notice:
- Extreme skin irritation or redness
- Difficulty breathing or swelling
- Severe dizziness or if side effects don’t go away
Tell your doctor about any allergies or skin problems before starting these treatments. If you’re pregnant or breastfeeding, talk about the risks with your doctor. This will help you make safe treatment choices.
Conclusion
Understanding scalp folliculitis is key to managing this skin issue well. Treatment often includes topical antibiotics like mupirocin and fusidic acid. These treatments are effective, especially for conditions like impetigo. Their role in treatment is crucial.
To manage scalp folliculitis well, balance is needed. It’s about mixing self-care with medical help. Keeping clean is crucial, but knowing when to get expert advice is just as important. This helps make treatments work better.
In the end, topical antibiotics are a big part of treating scalp folliculitis. Using the right methods improves scalp health and eases symptoms. This leads to better health overall.