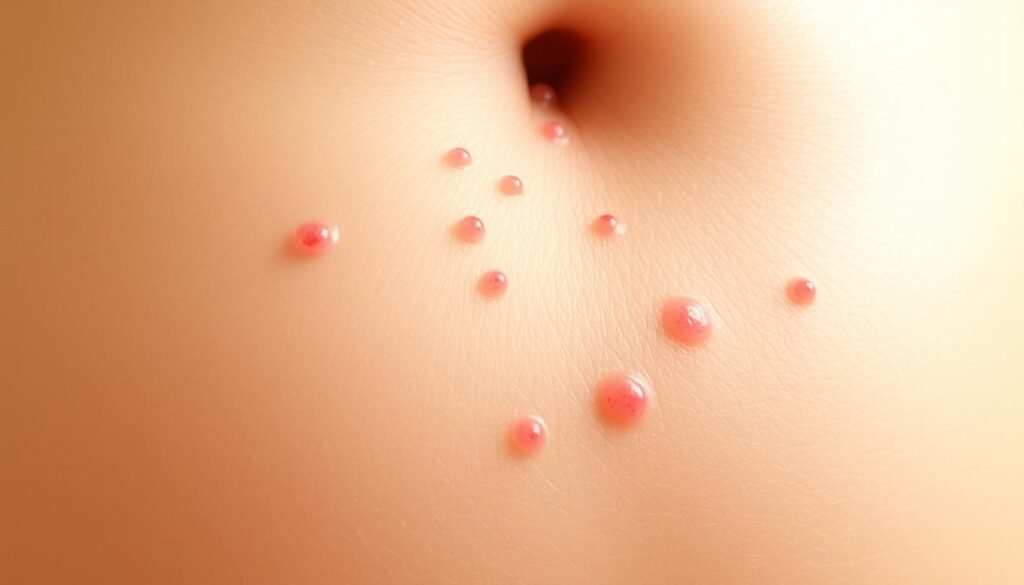
Did you know about 20% of adults face bacterial folliculitis around the pubic area in their lifetime? This condition, tied to *pubic hair infection*, comes from various causes and challenges those with *genital inflammation*. Learning about the causes, signs, and how to treat it is vital. This guide offers insights on effective treatments and *prevention tips* for healthy skin, especially after hair removal.
Key Takeaways
- Folliculitis is a common but often benign condition affecting the skin.
- Bacterial and fungal infections are the primary causes of folliculitis in the pubic area.
- Effective treatments range from topical creams to oral antibiotics, depending on severity.
- Home remedies and proper hygiene practices can alleviate mild cases.
- Seeking medical advice early can prevent complications associated with recurrent folliculitis.
- Preventive measures are key in maintaining healthy skin in sensitive areas.
Introduction to Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a skin condition that is quite common. It happens when hair follicles get inflamed or infected. Symptoms include small red bumps or blisters filled with pus. If not treated, it can lead to discomfort or even serious issues.
There are two main kinds of folliculitis: superficial and deep. Superficial types affect only a part of the hair follicle. Deep folliculitis, however, involves the whole follicle. Staphylococcus aureus bacteria often cause itchy, pus-filled bumps. “Hot tub folliculitis” comes from bacteria in poorly maintained hot tubs.
Pseudofolliculitis, or razor bumps, mainly occurs in people with curly hair. It happens when shaved hairs grow inward, causing irritation. Other types, like pityrosporum, gram-negative, and eosinophilic folliculitis, exist as well. They’re linked to different causes and affect specific groups of people.
Managing folliculitis usually involves good hygiene and self-care. Knowing the various types and potential complications is vital. For detailed treatment options and prevention tips, visit this link.
Understanding Folliculitis Pubic Area
Folliculitis in the pubic area happens when hair follicles get inflamed. Often, this inflammation is due to an infection or irritation. The root causes of folliculitis are quite varied. Among them, bacterial skin infections top the list, especially those by Staphylococcus aureus.
Other things like shaving too much, wearing tight clothes, and skin irritations also play a role. Knowing the usual symptoms of folliculitis is key in dealing with it well.
Definition and Causes of Folliculitis
The term “folliculitis pubic area” talks about the inflammation and infection of hair follicles in the groin. This issue comes from several sources, including:
- Bacterial skin infection, with Staphylococcus aureus at the forefront.
- Irritation caused by tight clothes or shaving.
- Harm to the skin like cuts or abrasions.
If you have diabetes, a weak immune system, or current skin infections, your risk is higher. Good hygiene and avoiding things that irritate are vital in cutting down risks.
Common Symptoms to Look For
If you have folliculitis in the pubic zone, you might see signs like:
- Red, inflamed bumps that look like a rash in the groin.
- Bumps that hurt, itch, or feel tender when touched.
- Pus-filled pustules that stick together in clusters.
- The skin around the follicles might crust or get irritated.
Seeing these symptoms means you should talk to a doctor. This will help avoid bigger issues like scarring or ongoing infections.
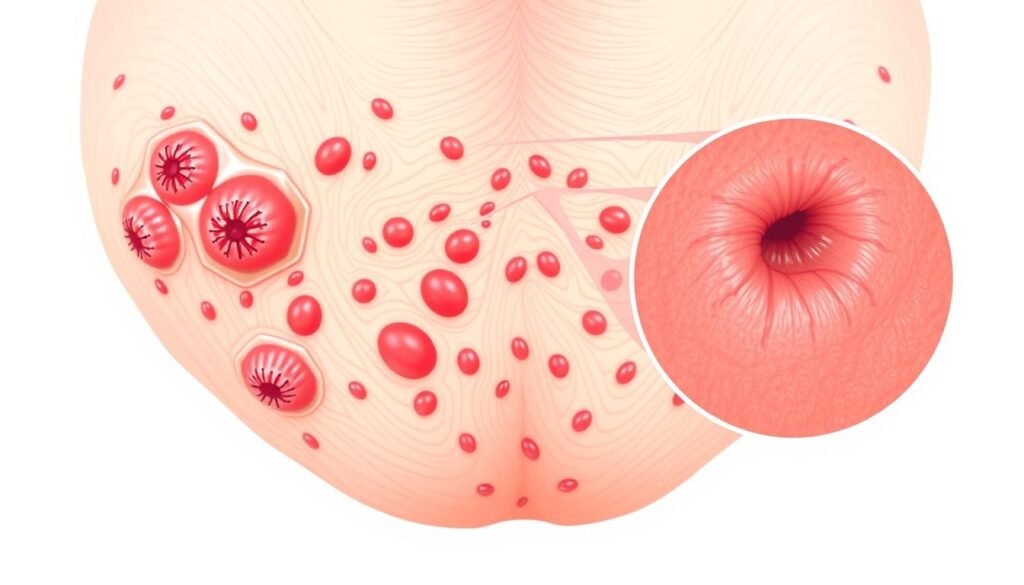
Types of Folliculitis Affecting the Pubic Area
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that affects different body parts, including the pubic area. It can arise from various causes, each leading to different types of folliculitis. Knowing these types helps in treating and preventing the condition effectively.
Bacterial Folliculitis
This type is mainly caused by Staphylococcus aureus. It’s the most common form. People usually get red bumps or pustules, looking much like acne. It often comes about after shaving or from skin friction, leading to so-called pubic hair infections. Doctors usually treat it with topical or oral antibiotics to fight the bacteria.
Fungal Folliculitis
Fungal folliculitis is usually linked to Malassezia yeast, affecting those prone to yeast infections. It looks a lot like acne, especially among teens in damp settings. To treat it, antifungal treatments are used, targeting the yeast responsible.
Pseudofolliculitis (Ingrown Pubic Hair)
Also known as ingrown pubic hair or razor bumps, pseudofolliculitis happens when hair grows back into the skin. It leads to inflammation. People with curly hair see it more, often from shaving wrong. By changing how one shaves and using soothing creams, the irritation can be lessened.
| Type | Cause | Common Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Folliculitis | Staphylococcus aureus | Pustules, red bumps | Topical/oral antibiotics |
| Fungal Folliculitis | Malassezia yeast | Red bumps, itching | Antifungal medications |
| Pseudofolliculitis | Ingrown hairs | Inflamed bumps, irritation | Soothing creams, hair removal adjustments |
Diagnosis of Folliculitis in the Pubic Region
To diagnose folliculitis, doctors use a step-by-step method. They start by checking the patient’s medical history. They look closely at how the person takes care of their personal hygiene. They also consider any skin irritations or infections they’ve had before. Knowing these things helps doctors make the right diagnosis.
Clinical Evaluation and History
Doctors first ask about the patient’s medical history when diagnosing folliculitis. They see if the person has had chronic skin issues, diabetes, or specific medications. These factors are important. They help find possible causes like being overweight or having a weak immune system. These can lead to skin problems.
Tests and Procedures
If doctors think it’s folliculitis, they use special folliculitis tests. Skin scraping checks for fungal infections. A bacterial culture identifies the bacteria causing the issue. Sometimes, a skin biopsy is needed. This checks for other skin diseases that look like folliculitis.
| Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Clinical Evaluation | Gather information about hygiene practices and personal history |
| Skin Scraping | Identify potential fungal infections |
| Bacterial Culture | Determine the exact bacteria causing folliculitis |
| Skin Biopsy | Rule out other skin conditions if needed |
Getting diagnosed quickly allows for the start of good treatment. It’s key to see a doctor if home care doesn’t work within a few days. For more details on folliculitis and how to manage it, visit this resource.
Effective Treatments for Folliculitis Pubic Area
Finding the right treatment for folliculitis in the pubic area is crucial. Various methods are available, such as topical treatments, oral antibiotics, and laser hair removal. These options help people make informed choices about their care.
Topical Treatments: Antibacterial Creams and Lotions
Topical treatments are the first step for mild folliculitis. Over-the-counter antibacterial creams, like mupirocin, offer relief. They should be applied directly to the affected areas to fight infections. It’s important to follow the healthcare provider’s usage instructions for the best results.
Oral Antibiotics for Severe Cases
In severe folliculitis cases, antibiotic treatment may be necessary. Oral antibiotics, such as cephalexin and dicloxacillin, target the bacteria causing infections. Consulting with a healthcare professional to find the right antibiotic regimen is key to effective management.
Alternative Treatments: Laser Hair Removal
Laser hair removal provides a long-term solution for pseudofolliculitis sufferers. It targets hair follicles, reducing hair regrowth and inflammation from ingrown hairs. Patients choosing laser hair removal can look forward to smoother skin and fewer folliculitis flare-ups.

| Treatment Type | Details | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Topical Treatments | Antibacterial creams applied directly to the skin | Effective for mild cases; quick relief |
| Oral Antibiotics | Prescribed for severe folliculitis | Effective in eradicating bacterial infections |
| Laser Hair Removal | Targets hair follicles to prevent growth | Long-term solution for reducing outbreaks |
Home Remedies and Self-Care Tips
Managing folliculitis at home can bring relief and help healing. Simple methods can ease discomfort and prevent more issues.
Warm Compresses for Relief
Warm compresses can really help the skin feel better. They soothe swollen areas and help drain lesions. Using warm compresses often encourages healing and comforts the skin.
Maintaining Proper Hygiene
Good hygiene is key for skin health and stopping folliculitis. Washing gently with antibacterial soap gets rid of harmful bacteria. Keeping the skin dry helps avoid further problems. Don’t share towels or razors to keep infections from spreading.
Over-the-Counter Solutions
Hydrocortisone cream can ease itching and swelling from folliculitis. It brings quick comfort. Soothing lotions keep the skin moist, aiding in healing. Hydrogen peroxide fights bacteria and fungi. Oils like tea tree and eucalyptus can also help with symptoms.
Prevention Tips for Folliculitis in the Groin
Keeping the groin area free from folliculitis starts with good hygiene and skin care. Following the right steps can lower the risk of getting this common issue. Knowing how to keep your skin healthy is key to staying comfortable and avoiding problems.
Intimate Hygiene Practices
Good intimate hygiene is vital for preventing folliculitis. Washing regularly with a gentle soap keeps the area clean. Making sure the skin stays dry is also crucial. Wearing breathable underwear helps manage moisture, which is good for your skin’s health. Shower with antibacterial soap after sweating or working out to wash away bacteria.
Smart Hair Removal Practices
When removing hair, it’s smart to use clean, sharp razors and shave in the direction the hair grows. Exfoliating before you shave can help stop pores from clogging and prevent ingrown hairs. Using electric razors or trimmers can also lower the chance of irritation.
Keeping Skin Healthy and Irritation-Free
Keep your skin healthy by moisturizing regularly. This helps stop dryness and irritation. Avoid tight clothing to reduce friction and keep your skin safe. Exfoliating every week helps prevent follicles from getting blocked. This cuts down on ingrown hairs and folliculitis. These simple steps are great for your skin’s overall health and comfort.
| Prevention Technique | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Intimate Hygiene | Regular washing with mild soap and keeping the area dry. | Reduces bacteria; helps prevent folliculitis. |
| Shaving Tips | Use sharp razors and shave in the hair growth direction. | Minimizes irritation and ingrown hairs. |
| Moisturizing | Apply moisturizer regularly to prevent dryness. | Keeps skin healthy and irritation-free. |
| Exfoliating | Regularly exfoliate to prevent clogged follicles. | Reduces risk of bumps and folliculitis. |
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to get medical help for folliculitis is key to avoiding worse symptoms and problems. You should watch for signs that suggest you need a doctor’s advice. If home remedies don’t work, or if things get worse, it’s important to get professional help.
Identifying Severe Symptoms
Some serious infection signs include:
- Spreading redness around the affected area
- Increased pain that doesn’t go away
- Fever with the rash
- Persistent or recurrent bumps despite treatment
When you see these signs, it’s critical to seek medical care quickly. This helps prevent folliculitis complications like repeat infections or lasting scars.
Consulting a Dermatologist
If folliculitis keeps bothering you, seeing a dermatologist might be the next step. Skin experts can offer specific folliculitis treatment plans. They help tell apart other skin issues that look like folliculitis. They might suggest prescription medicine or other serious treatments in tough cases. For tips on handling skin issues, people can find more info on avoiding triggers to prevent folliculitis flare-ups.
Conclusion
Folliculitis in the pubic area can be managed well with the right knowledge. Knowing its causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial. This helps in taking steps to keep the skin healthy and lower the chance of it coming back. Quick action is important for effective treatment, and spotting symptoms early leads to better healing.
Preventing folliculitis is also key. This includes staying clean, shaving carefully, and using clean hot tubs. If you keep having issues, it’s smart to see a doctor. They can offer treatments that fit your needs, keeping your skin at its best. For tips on spotting folliculitis, check out this guide on recognizing and treating folliculitis.
To really make a difference, combine good management with ongoing prevention. This uplifts your life quality and stops folliculitis problems. Being informed and acting wisely are essential for keeping sensitive skin areas healthy.