About 67% of people under 50 have HSV-1, which causes oral herpes. This fact shows how common herpes is worldwide. However, many people confuse herpes with folliculitis, which is inflammation of hair follicles from irritation. Knowing the specific symptoms of each condition is key for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Herpes might cause painful blisters and general sickness symptoms like fever. It’s important to know the difference between herpes and folliculitis. Folliculitis appears as red bumps or pus-filled spots. Recognizing their distinctive features helps manage potential outbreaks and keeps your skin healthy.
Key Takeaways
- Over two-thirds of adults under 50 have HSV-1, highlighting the importance of awareness about herpes symptoms.
- Folliculitis commonly impacts areas where hair grows, especially under conditions of sweat and friction.
- Understanding the differences in symptoms can help differentiate herpes vs folliculitis more effectively.
- Herpes outbreaks may involve flu-like symptoms and can have severe complications if left untreated.
- Proper hygiene and skin care practices are essential in preventing both conditions from worsening.
Understanding Folliculitis
Folliculitis is when hair follicles get inflamed, causing red, painful bumps. These bumps may fill with pus. They often appear in hairy areas like the chest, face, and private parts. To treat it well, we need to know why it happens. It may be due to shaving, tight clothes, or infections.
What is Folliculitis?
Folliculitis starts from irritated or infected hair follicles. It looks like small, pus-filled spots that can itch or hurt. Things like shaving, waxing, being overweight, and sweating a lot can cause it. Pseudofolliculitis barbae is one kind. It happens from shaving. It mostly affects men with dark skin and curly hair.
Common Types of Folliculitis
Folliculitis comes in infective and non-infective kinds. Bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus can cause it. So can a bacteria found in hot tubs, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Yeasts and mites can also be culprits. Each type affects how we treat it:
| Type | Causes | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Folliculitis | Staphylococcus aureus | Antibiotic ointments or tablets |
| Hot Tub Folliculitis | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Antibiotics and warm compresses |
| Yeast Folliculitis | Malassezia yeasts | Antifungal treatments |
| Pseudofolliculitis Barbae | Shaving irritation | Proper shaving techniques and creams |
| Eosinophilic Folliculitis | Immune suppression | Medication to improve immune response |
With the right care, most folliculitis cases get better on their own. Knowing the cause is key to handling it well and avoiding worse problems like scars or big infections.
Understanding Herpes
Herpes is mainly caused by the herpes simplex virus, leading to outbreaks like painful lesions. These can appear as oral or genital herpes, with each type showing different symptoms. There are two main types of herpes simplex virus responsible for these infections.
What is Herpes?
The herpes simplex virus causes this infection. It stays inactive in the body until triggered. Stress or sickness can cause outbreaks, often signaled by a prodrome phase. Symptoms like fever, chills, muscle aches, and fatigue may appear before the lesions do. Outbreaks usually affect areas with thin, moist skin, such as the genitals and mouth.
Types of Herpes Simplex Virus
People should know about two main types of herpes:
- HSV-1: It mainly causes oral herpes, with cold sores or fever blisters around the mouth.
- HSV-2: It’s mostly linked to genital herpes, leading to outbreaks in the genital area.
Herpes spreads through direct skin contact, even without visible symptoms. Around 67% of individuals under 50 have HSV-1. Meanwhile, about 11% carry HSV-2.
| Herpes Type | Common Symptoms | Typical Location | Prevalence Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSV-1 | Cold sores, fever blisters | Oral region | 67% (under 50) |
| HSV-2 | Genital lesions | Genital area | 11% |
Differences Between Folliculitis and Herpes
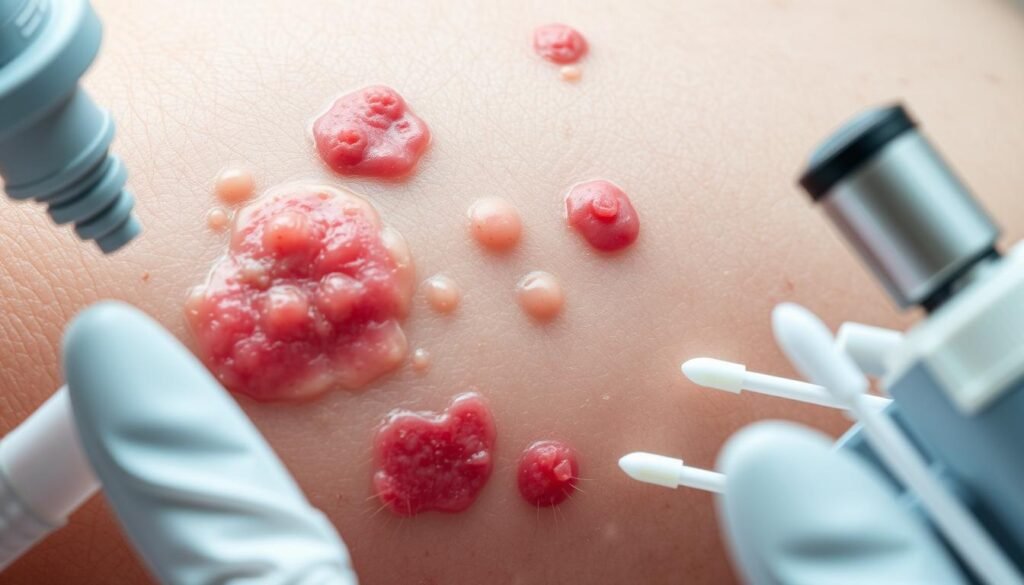
It’s important to know the differences between folliculitis and herpes for the right treatment. You can tell them apart by the visual symptoms they show. Also, knowing how you can catch each helps prevent them. Folliculitis looks like red, swollen spots on your skin. Herpes, however, shows up as groups of sore blisters. Spotting folliculitis symptoms early is key to getting help fast.
Visual Comparison of Symptoms
Folliculitis appears as red spots that might be slightly swollen around. These spots can be filled with pus and often itch. On the flip side, herpes is marked by painful blisters that usually group together. Noticing how they look can help you figure out what you might have. For pictures to help you compare, see herpes vs folliculitis.
Understanding Transmission Methods
How you get these conditions is very different. Folliculitis can come from bacteria or fungi, triggered when hair follicles get irritated or hurt. This might happen from tight clothes or shaving. Herpes, though, spreads mostly through direct contact with skin, especially during close physical moments. For more help on identifying folliculitis symptoms, have a look at this guide.
Symptoms of Folliculitis
It’s important to spot the symptoms of folliculitis early. This condition starts with small red bumps around hair follicles. These bumps can turn into whiteheads or pus-filled centers as the condition gets worse. This can cause itching and soreness. Catching these signs early helps in managing the condition.
Early Signs of Folliculitis
Early symptoms of folliculitis include:
- Small red or inflamed bumps around hair follicles
- Pus-filled blisters that may form whiteheads
- Itching and tenderness in the affected areas
Areas Most Affected by Folliculitis
Folliculitis can happen anywhere on the body where hair grows. The most common areas affected include:
| Body Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Scalp | Can lead to itchy patches or bumps in the hair. |
| Beard Area | Common in individuals who shave, potentially causing irritation. |
| Neck and Armpits | Areas prone to friction and moisture, facilitating infection. |
| Groin | Susceptible to irritation and infrequent hygiene. |
| Legs | Visible symptoms may appear after shaving or waxing. |
If you don’t treat folliculitis, it can lead to clusters of painful sores. Knowing these symptoms is key for fast and effective treatment.
Symptoms of Herpes
Herpes has specific signs that help recognize an outbreak. Its main sign is herpes blisters. These blisters create clusters filled with fluid, causing discomfort. Before these blisters appear, one might feel tingling, itching, or burning. Spotting these early signs helps manage the infection.
Characteristics of Herpes Blisters
Herpes blisters go through distinct stages. At first, the area looks red and swollen. Then, small bumps emerge, turn into vesicles, and finally painful ulcers. This blistering phase lasts about 2 to 3 weeks. The last phase, crusting, means healing. Knowing this process helps people understand what to expect during an outbreak.
Associated Systemic Symptoms
Herpes also causes systemic symptoms during outbreaks. These include:
- Fever
- Muscle aches
- Swollen lymph nodes
These signs show the body’s broad reaction to the virus. This highlights the seriousness of herpes infections. It’s important for individuals with herpes to watch for these systemic signs. They often mean a stronger immune response, especially in initial outbreaks.
Causes and Risk Factors
Folliculitis and herpes are complex skin conditions. They differ in causes and risk factors. For example, folliculitis is a skin issue that happens for many reasons. In contrast, herpes is a result of a viral infection.
Causes of Folliculitis
Folliculitis comes from damaged hair follicles. This damage leads to inflammation. It can be caused by:
- Shaving and friction from clothing
- Bacterial infections, primarily Staphylococcus aureus
- Fungal infections
- Use of certain medications like corticosteroids
- Hot tub exposure to inadequately maintained water
- Risk factors for folliculitis include obesity, diabetes, and lack of proper hygiene.
Barber’s itch targets those with facial hair. It’s particularly common among people who shave often. For detailed info on folliculitis, check out this site.
Causes of Herpes
Herpes is mainly because of the herpes simplex virus. There are two main types of this virus. These cause different herpes infections.
- Direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person during outbreaks
- Sharing personal items like towels or razors
- Risk factors for herpes include a weakened immune system and having multiple sexual partners.
Knowing these factors helps in prevention and treatment. Being aware is key to avoiding infection.

Diagnosis Techniques for Folliculitis
A healthcare provider looks at the skin to start diagnosing folliculitis. They search for red bumps and swelling near hair follicles. They also ask about the patient’s recent activities and use of certain products.
Visual Examination Process
During the visual examination, specialists check for:
- Redness and inflammation around hair follicles
- Pinpoint red bumps or pustules
- Presence of nodules, particularly in deeper folliculitis cases
They use this information to identify the folliculitis type. They decide if more steps are required.
Laboratory Tests for Folliculitis
For tough or recurring cases, doctors may suggest lab tests. These include:
| Test Type | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Swab Cultures | Samples taken from affected areas | To identify bacterial or fungal infections |
| Skin Biopsy | Removal of a small skin sample for examination | To rule out other skin conditions |
These tests help pinpoint the cause of folliculitis. Knowing the cause lets doctors treat it effectively. This lowers the risk of serious problems like permanent hair loss or scarring.
Diagnosis Techniques for Herpes
It’s crucial to accurately diagnose herpes for effective treatment and symptom management. The diagnosis process includes evaluations and lab tests to confirm the virus’s presence.
Visual and Symptomatic Evaluation
The first step in diagnosing herpes involves checking symptoms closely. Doctors look for blisters and sores near the mouth and genitals. They also check for fever, tiredness, and swollen glands. Important to note, herpes can spread even without visible sores.
Laboratory Tests for Herpes
To be sure it’s herpes, several tests are needed. Here are the common ones:
- HSV Culture Test: This involves taking a sample from a blister or sore to find the virus.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Test: This test looks at DNA to tell apart HSV-1 and HSV-2, giving quick and precise results.
- Blood Tests: These tests look for antibodies when there are no sores. However, they might not show anything right after the first outbreak and need careful reading.
Knowing the different tests helps manage herpes effectively. Early detection means better control, lowering the risk of spreading it and reducing severe effects of the virus.
| Type of Test | Purpose | Timing |
|---|---|---|
| HSV Culture Test | Identifies active herpes infection from lesions | During an outbreak |
| PCR Test | Provides rapid identification of HSV type | During or shortly after an outbreak |
| Blood Test | Detects antibodies against HSV | Anytime, but may not be positive right after infection |
Herpes or Folliculitis: Identifying the Symptoms
Knowing how to tell herpes and folliculitis apart is key. They have different symptoms and appear at different times. These signs help people figure out which one they might have. It’s important because it affects how the condition is treated.
Key Differentiators of Symptoms
Herpes and folliculitis look and feel different. Herpes forms painful blisters. Folliculitis looks like pus-filled bumps near hair. Herpes shows up on softer, moist skin areas. Folliculitis can be found on thighs and buttocks. The fluid from herpes is watery, but from folliculitis, it’s thicker.
Timing of Symptom Onset
Folliculitis can appear within hours or by the next day. Herpes takes longer, around 2 to 4 days to show up. This helps in figuring out which issue it might be.
Spotting these differences early is crucial for better health results. For more info, check this resource. It goes into more detail about both conditions.
Treatment Options for Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a skin issue that many people face. It’s important to tackle it early. There are many ways to treat it, like home remedies and store-bought options. Taking action quickly helps avoid serious problems and heals faster.
Home Remedies and Over-the-Counter Options
There are easy home treatments for folliculitis. These methods can help ease the symptoms:
- Warm compresses: Putting a warm, wet cloth on the skin eases irritation and helps healing.
- Antiseptic solutions: Products from the store, including antiseptics or creams with benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid, can lower swelling and fight off infection.
- Proper hygiene: Keeping the skin clean is key. Use gentle soaps regularly to keep infections at bay.
- Loose-fitting clothing: Stay away from tight outfits that can upset the skin. Clothes that let your skin breathe help a lot.

When to Seek Professional Help
Sometimes, folliculitis won’t get better by itself. It’s crucial to ask a doctor for help in these situations:
- If symptoms stick around or get worse after trying home care.
- When you experience severe pain, swelling, or fever.
- If you keep getting folliculitis, which might mean there’s a deeper problem.
- If the infected skin looks very red or has pus.
Choosing the right treatment for folliculitis is very important for recovery. Catching it early and taking action leads to good outcomes.
Treatment Options for Herpes
Managing herpes includes using antiviral medications as a key strategy. These drugs aim to lessen how often and how severe the outbreaks are. They provide significant support for those dealing with herpes.
Overview of Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications are crucial for herpes treatment. Doctors often prescribe acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir. Acyclovir is well-known for fighting the herpes simplex virus. It stops the virus from multiplying, which reduces the outbreak’s impact.
Starting treatment early during an outbreak makes these drugs work better. This leads to a quicker recovery and less severe symptoms.
Pain Management Strategies
Dealing with pain is also vital in managing herpes. Over-the-counter pain relievers, like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can ease the pain. Making small changes in your lifestyle helps too. For example, wearing loose clothes reduces skin irritation.
For more in-depth treatment info, check out this resource. Using antiviral treatments and pain management together improves life quality for those with herpes.
Conclusion
When we wrap up the discussion, it’s vital to know the difference between herpes and folliculitis. This helps in proper diagnosis and treatment. Herpes usually shows up as painful blister clusters. Meanwhile, folliculitis looks like itchy, pus-filled bumps that might scar.
Herpes is a contagious virus spread mainly through close contact. On the other hand, folliculitis is caused by irritated or infected hair follicles and isn’t contagious. Both conditions, however, can have serious complications if not treated. Herpes increases the risk of more sexually transmitted infections, while folliculitis can cause scarring and more infections.
It’s pivotal for anyone with symptoms of either condition to see a healthcare provider quickly. Early help often means a better chance of preventing serious problems. It also ensures care that fits the person’s specific needs. Knowing about both conditions empowers people to get help when they need it.
