Did you know that some kinds of folliculitis can spread through everyday activities? About 10% of cases come from bacterial infections like Staphylococcus. This skin rash happens when hair follicles get inflamed or infected. People often wonder if it can spread to others.
While many types of folliculitis aren’t likely to pass on, some can. For example, the herpes simplex virus causes a type that spreads through direct skin contact or bodily fluids. It’s essential to know how these infections work. This knowledge helps keep our skin healthy and lowers the chances of spreading them.
Key Takeaways
- Most cases of folliculitis are not contagious, but some types, like bacterial folliculitis, can be.
- Hot tub folliculitis, caused by Pseudomonas bacteria, spreads through contaminated water.
- Fungal folliculitis may recur and can also pose a contagion risk in chronic cases.
- Individuals with weakened immune systems or skin injuries are at a higher risk for developing folliculitis.
- Prompt medical attention is advised if home remedies do not improve symptoms.
Understanding Folliculitis
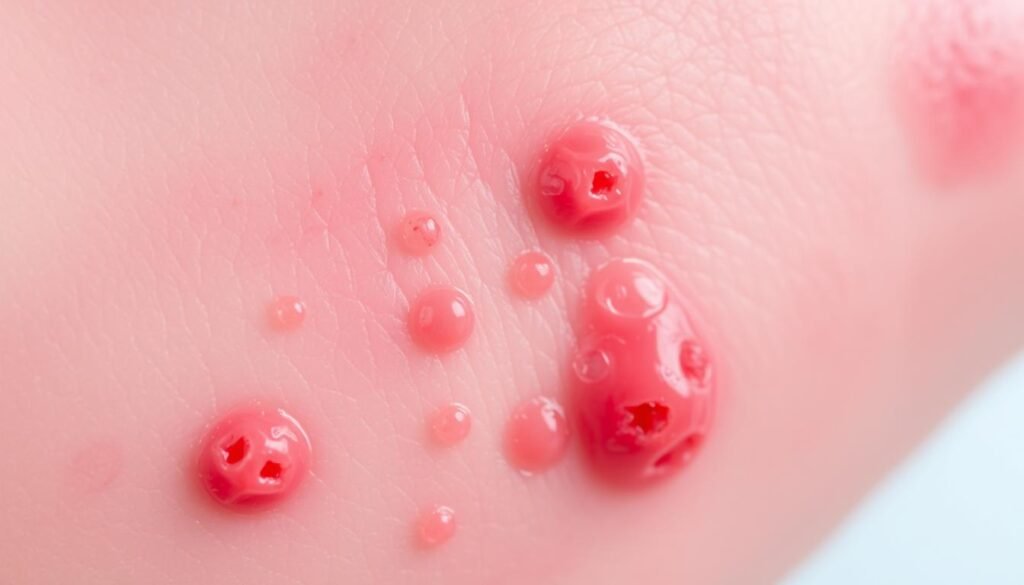
Folliculitis is a skin condition that appears as an infection in hair roots. It leads to folliculitis symptoms such as red, swollen spots. These can itch or feel tender. It can happen anywhere on the body with hair, causing skin trouble.
Many things can cause this. Cutting hair close to the skin, tight clothes, or sweating a lot are common triggers. People with health issues like diabetes or weak immune systems are more at risk. Knowing these causes helps in avoiding folliculitis.
Some notable forms include:
- Bacterial Folliculitis: Caused primarily by Staphylococcus aureus.
- Hot Tub Folliculitis: Linked to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, often from unclean water.
- Fungal Folliculitis: Comes from a fungus called Malassezia, affecting oily areas.
- Viral Folliculitis: Often from the herpes virus.
- Demodex Folliculitis: Tiny mites like Demodex folliculorum cause it.
Spotting symptoms early is key. While most cases get better fast with the right treatment, bad cases can cause bigger problems. These include deep skin infections, scars, or losing hair for good. Knowing about folliculitis helps people deal with it better and get help when needed.
| Type of Folliculitis | Cause | Common Symptoms | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Folliculitis | Staphylococcus aureus | Red, swollen bumps | Topical antibiotics |
| Hot Tub Folliculitis | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Itchy, painful lesions | Oral antibiotics |
| Fungal Folliculitis | Malassezia species | Itchy patches | Oral antifungal agents |
| Viral Folliculitis | Herpes virus | Fluid-filled blisters | Antiviral medications |
| Demodex Folliculitis | Demodex folliculorum | Redness and itching | Topical permethrin |
What Causes Folliculitis?
Folliculitis can start in many ways. Knowing why it happens is key to treating it right. Often, it’s due to a bacterial infection. The usual culprit is Staphylococcus aureus. This germ can get into hair follicles through small cuts. These infections lead to red, sometimes itchy bumps.
Blocked skin is another main cause. This can happen when dead skin piles up or from heavy makeup use. Blockages make it easier for your skin to get inflamed. Pseudomonas folliculitis, linked to unclean hot tubs, shows up within a day or two of being exposed to Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria.
Some conditions, like razor bumps, are more common in those with curly beards who shave close. This often leads to ingrown hairs and inflammation. Then, there’s pityrosporum folliculitis, which is a yeast infection. It mainly affects your back and chest.
Long-term antibiotic use for acne might lead to gram-negative folliculitis. People with HIV/AIDS might face eosinophilic folliculitis, though its exact cause is still unknown. Understanding these triggers helps in avoiding them and choosing the right treatment.
For more information on handling this issue, check out this resource. Knowing the different reasons folliculitis happens helps in managing the symptoms well. It also aids in preventing it from coming back.
Types of Folliculitis
Folliculitis comes in various forms, each with unique signs and treatments. Knowing about these helps in dealing with and stopping folliculitis.
Bacterial Folliculitis
Bacterial folliculitis is pretty common. It shows up as groups of red bumps and blisters with pus. It’s mainly caused by the Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. This problem can pop up anywhere on the body where there’s hair, like on your face, neck, or back.
Things like shaving, tight clothes, and sweating a lot can make it worse. To lower your risk, keep clean and shave carefully.
Fungal Folliculitis
Fungal folliculitis is from yeast infections and looks like itchy, pus-filled spots. It usually needs antifungal medicine to clear up. Using lotions can help by keeping your skin moist and less annoyed.
Try to avoid places that are very hot and wet, as these can help fungi grow and cause folliculitis.
Viral Folliculitis
Viral folliculitis is not as common but happens due to viruses like herpes simplex. This kind leads to sore, red hair follicles that look like swollen bumps. Even though it’s rare, touching things with the virus on them or direct contact with herpes sores can increase the risk.
For more details and advice on how to tackle serious folliculitis cases, look into this resource.
| Type of Folliculitis | Causes | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Folliculitis | Staphylococcus aureus | Red bumps, pus-filled blisters | Topical antibiotics |
| Fungal Folliculitis | Yeast infections | Itchy pustules | Antifungal medications |
| Viral Folliculitis | Herpes simplex virus | Swollen, inflamed hair follicles | Antiviral medications |
Folliculitis Contagious: An Overview
Is folliculitis contagious? This question matters when we talk about skin conditions and how they spread. Usually, folliculitis doesn’t jump from one person to another easily. The main bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus, is often just living peacefully on our skin. But, the risk of passing it on increases with hot tub folliculitis. This type happens in hot tubs that aren’t clean, affecting several people at once.
Then, there are unique types like eosinophilic folliculitis and Malassezia folliculitis. They show up in certain groups. For example, young boys in humid places or men with HIV. Knowing the different kinds of folliculitis and what sparks them is key.
Folliculitis is usually no big deal but can sometimes get worse, needing antibiotics or even laser hair removal. To avoid it, take good care of your skin. Stay clean, keep moisturized, and shave right. Don’t share personal items and keep clean, especially where lots of people gather.

| Type of Folliculitis | Common Triggers | Contagious Potential | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Tub Folliculitis | Pseudomonas bacteria in poorly maintained hot tubs | Possible in shared environments | Warm compresses, antibiotics if severe |
| Malassezia Folliculitis | Humidity, yeast overgrowth | Not typically contagious | Topical antifungals |
| Eosinophilic Folliculitis | Associated with HIV | Generally not contagious | Consultation required for treatment |
| Furuncles (Boils) | Deeper hair follicle infections | Can spread through contact | Antibiotics may be necessary |
When is Folliculitis Contagious?
Folliculitis usually doesn’t pass from person to person. Most of the time, it stays with one person. But some conditions can spread it. Knowing these can help avoid any risk.
Hot Tub Folliculitis
Hot tub folliculitis comes from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in water. It happens mainly in pools and tubs that aren’t clean. Keeping these places clean can lower the risk of catching this contagious skin rash.
It’s smart to be careful in public pools and hot tubs. This is especially true if you use them a lot.
Staphylococcal Folliculitis
Staphylococcal folliculitis spreads by touching someone with it or using their things. Razors are a common item that can pass it on. Be extra careful if you have cuts or weak skin. Avoid touching people with infections or their stuff.
Folliculitis caused by Herpes Simplex Virus
This type spreads by close contact or using the same utensils. It’s tricky because it can spread even without visible signs. If you’re close to someone, be careful.
For more details on folliculitis types and how to prevent them, click this informative link.
How Folliculitis Spreads
Knowing how folliculitis spreads is key to stopping it. Close skin contact greatly increases the spread of this skin issue. People with scrapes or open sores are at high risk. That’s because bacteria find it easy to enter the skin through these open areas. By keeping clean, we can lower the chances of giving folliculitis to others, especially in social settings.
Close Skin Contact
Skin-to-skin contact can pass infectious agents to others. This happens during activities like sports or workouts where people share equipment. Having an open wound and doing these activities raises the risk of spreading folliculitis.
Sharing Personal Items
Sharing personal things is another way folliculitis spreads. Items such as towels, razors, and clothes can carry bacteria and fungi. To cut down the risk, don’t share these items. Make sure to clean them well. Staying clean plays a big part in stopping folliculitis.

Common Symptoms of Folliculitis
Folliculitis shows symptoms that help spot it early. Knowing these folliculitis symptoms is key to avoid worse problems and get help in time. You might see red, swollen bumps around hair follicles, sometimes with pus. These signs are critical to grasp the infection’s nature and how bad it is.
Identifying Infected Hair Follicles
Spotting infected hair follicles is crucial for right care. Look out for:
- Red and inflamed bumps
- Pus-filled blisters at the hair’s root
- Itching or burning feelings
- Pain and tenderness in the area
Keeping an eye on these symptoms is vital. They can show if the folliculitis is from bacteria, fungi, or other causes. Catching it early means you can manage it well and prevent big problems.
Differences between Folliculitis and Acne
Knowing the difference between acne versus folliculitis helps with treating them. Both might have red bumps, but they’re not the same. Here’s how:
| Feature | Folliculitis | Acne |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Often around hair follicles, like on the face, neck, and buttocks | Usually on the face, back, and shoulders |
| Pus Presence | Often has pus in the bumps | May have blackheads or whiteheads, usually without pus |
| Causes | Due to infections, rubbing, or hair growing wrong | Caused by hormone changes, blocked pores, and bacteria |
| Treatment | May use creams for bacteria or fungi | Often treated with special creams or hormone help |
Understanding these differences helps get the right treatment early. This can lower the risk of troubles from each condition.
Risks Factors for Developing Folliculitis
Knowing the folliculitis risk factors is key to avoiding this skin problem. Some people are more prone to it due to certain conditions. For example, those with diabetes may have weaker skin, while those with a weak immune system face a greater infection risk.
Shaving often also adds to the risk. It can irritate and open up the hair follicles. This makes it easy for Staphylococcus aureus bacteria to get in and cause trouble. Wearing tight clothing can also harm the skin by causing pressure and friction.
Dirty hot tubs and pools are risky too. They can be full of germs, especially in places like spas. Obesity is another factor, as more body weight can mean more skin friction. This can increase the chance of getting folliculitis.
If you wear sweaty clothes for too long, it can also cause problems. It’s important to understand these risk factors well. By knowing and tackling the health and lifestyle issues that make your skin vulnerable, you can better avoid folliculitis.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Diabetes | Compromises skin integrity and increases susceptibility to infections. |
| Weakened Immune System | Conditions like HIV or cancer can reduce the body’s ability to ward off infections. |
| Frequent Shaving | Irritates hair follicles and opens pathways for bacterial infection. |
| Tight Clothing | Exposes skin to friction, increasing the likelihood of irritation and infection. |
| Unclean Hot Tubs | Presence of bacteria such as pseudomonas increases risk of hot tub folliculitis. |
| Obesity | Increased skin friction raises the chance of developing folliculitis. |
| Improper Hygiene | Failure to maintain good hygiene after sweating or swimming fosters infection. |
Treating Folliculitis
Folliculitis comes in two main types: non-infective and infective. Each type needs a different way to be treated. It’s key to know how to handle this condition for a fast recovery. Mild cases might get better with home care, but serious cases could need doctor’s help.
Home Remedies
Using simple home remedies can greatly improve folliculitis symptoms. Some helpful methods include:
- Warm compresses: Putting a warm, moist cloth on the sore spot can ease pain and help heal.
- Antiseptic washes: Using antibacterial washes available in stores can keep skin bacteria in check, lowering infection chances.
- Shaving techniques: Shaving correctly with a sharp razor and following the hair growth can stop more irritation and ingrown hairs.
Medical Treatments
If home treatments don’t work, it’s time to seek medical options. The doctor might suggest:
- Antibiotics: To fight bacterial infections, doctors may prescribe antibiotics. These can come as lotions, gels, or pills.
- Antifungal medications: For infections caused by yeast, creams or oral medications are usually the go-to solutions.
- Steroid creams: To reduce inflammation linked with eosinophilic folliculitis, steroid creams might be used.
Should your symptoms not improve or get worse, seeing a healthcare provider is important. They will find out the cause and tell you how to treat your folliculitis right.
Folliculitis Prevention Tips
Keeping your skin healthy and avoiding irritation is key in preventing folliculitis. Simple steps in skin care and hygiene can make a big difference. Here are some helpful tips.
- Keep the Skin Clean: Wash your skin with gentle antibacterial soap to remove oil and bacteria.
- Moisturize: Use a non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep the skin moist, preventing irritation.
- Choose Loose Clothing: Pick clothes that are loose. They won’t rub your skin the wrong way, especially in sensitive areas.
- Use Clean Shaving Equipment: Make sure razors and shaving creams are clean. It helps avoid irritation and infections.
- Practice Safe Swimming: Always keep clean after being in hot tubs or swimming pools to lessen infection risks.

Always be mindful of personal cleanliness to prevent folliculitis. Watch your skin for any unusual signs. Addressing them quickly is crucial. Knowing what causes skin issues helps you avoid them.
Is Folliculitis a Sexually Transmitted Infection?
Many people wonder if folliculitis is an sexually transmitted infection. But it’s not classified as one. However, it’s easy to get confused. Folliculitis mainly comes from skin bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus. Yet, it can look like some STIs, especially herpes.
Folliculitis can happen to anyone and is crucial to note. Conditions like herpes can cause bumps that look like folliculitis. Herpes transmits through close contact and has two types, HSV-1 (lips) and HSV-2 (genitals). This makes it important to understand the difference for proper treatment.
Keeping clean is key to avoid folliculitis and related risks. Knowing how it spreads reduces worry about catching it. Though not contagious, the bacteria behind folliculitis can move from person to person. This happens through direct contact or shared items like razors or towels.
| Condition | Transmission Method | Common Symptoms | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Folliculitis | Non-contagious; may spread via bacteria through skin contact or shared items | Itchy, pus-filled bumps | Any hair-covered area |
| Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV 2) | Sexual contact or intimate skin contact | Fluid-filled blisters, pain, itchiness | Genital and surrounding areas |
It’s important to focus on prevention and learn the differences. For more info on folliculitis causes and treatment, read this link.
Conclusion
Folliculitis is a common skin problem that anyone can get, no matter their age or gender. Many people will face it at some point in their lives. It’s key to know about its causes, symptoms, and types to manage it well. For example, hot tub folliculitis comes from not-so-clean pools. Also, pityrosporum folliculitis is due to too much yeast on the skin.
It’s important to tell the different kinds of folliculitis apart, like gram-negative or eosinophilic pustular folliculitis. Understanding these can point you to the right treatments and how to avoid getting it again. Something as simple as staying clean, wearing comfy clothes, and safe shaving can make a big difference. These easy steps help stop folliculitis from happening.
Staying ahead with skin care is key to keeping conditions like folliculitis in check. Talking to a doctor can help you find the best way to look after your skin. This personal plan helps keep your skin in good shape and controls flare-ups. For more info on managing folliculitis effectively, check out this helpful link: effective skin health management.